Blastomycosis-Like Pyoderma- A Rare Case Report
Amrita A. Hongal1, Somashekar Gejje2
1 Dermatologist, The Bangalore Hospital, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India.
2 Plastic Surgeon, The Bangalore Hospital, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India.
NAME, ADDRESS, E-MAIL ID OF THE CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: Dr. Amrita A Hongal, Consultant Dermatologist, The Bangalore Hospital, #202, R V Road, Bengaluru 560004, Karnataka, India.
E-mail: amritahongalleo@gmail.com
Blastomycosis-like pyoderma is a rare, cutaneous bacterial infection of skin, seen in malnourished individuals, in a poor state of health and manifests as vegetating skin lesions. It is an unusual tissue reaction possibly to bacterial infection, the most common organism being Staphylococcus aureus.
This case report is of a 35-year-old male who presented with thick verrucous surfaced plaques and papules on trunk and extremities since 2 months. Investigations revealed anaemia with hypochromasia, neutrophilic leucocytosis, hypo-proteinemia and hypo-albuminemia with reversal of A/G ratio. Pathergy test was negative. Pus on Gram’s stain showed plenty of pus cells, and negative for AFB and fungal stain. On culture of pus grew Coagulase negative staphylococcus species. Biopsy showed acanthosis of epidermis with moderate lymphocytic infiltrates in dermis and focally a few neutrophils and histiocytes. Patient fulfilled the criteria for diagnosis of blastomycosis like pyoderma viz., presentation of large verrucous plaques with pustules and ulcers with elevated border, histologically neutrophilic infiltration and growth of one pathogenic bacterium on culture. Patient responded to long-term cefotaxime therapy.
Blastomycosis-like pyoderma, Coagulase negative staphylococcus species, Malnutrition
Case Report
A 35-year-old male patient, from a low socio-economic status and in a poor state of hygiene presented with skin lesions over chest, upper and lower limbs since 2 months, associated with mild pain. Patient gave positive history of alcohol intake and smoking, since 17 years. He was taking oral and topical medication for 2 weeks with no improvement. There was no history of trauma, consumption of bromides/iodides, tuberculosis or contact with tuberculosis.
Patient was pale and malnourished, with normal vital parameters. There was pitting non-tender pedal edema, with bilateral inguinal lymphadenopathy. Cutaneous examination revealed multiple, bilateral, symmetrical, thick grayish verrucous plaques with heavy crusting and ulcers with elevated borders, ranging from 2-10cm in size, distributed over the mammary area, shoulders, arms, extensors of forearm, hands, lateral aspect of thighs, legs and dorsum of feet [Table/Fig-1a-c]. Removal of crusts revealed ulcers with foul swelling purulent exudates. Systemic examination was normal.
(Multiple small vegetative growths over upper limbs and a few ulcers over Right arm,1b: Vegetative plaques over lower leg,1c:crusted ulcers over the mammary area.
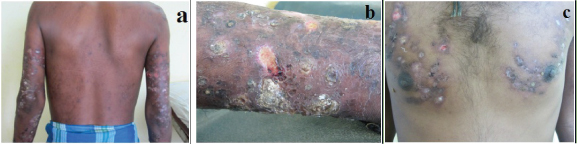
Investigations showed anaemia (9.0 g/dl) with hypochromasia, neutrophilic leucocytosis, hypo-proteinemia and hypo-albuminemia with reversal of Albumin Globulins (A/G) ratio. Blood sugar, serum electrolytes and RFT were normal. Urine and stool examination were normal. Mantoux test and Pathergy test was negative. HIV 1 and 2 and Hbs Ag were non-reactive. Chest X-ray and Ultrasound (USG) abdomen was normal. Smear examination on gram’s stain showed plenty of pus cells, and negative for Ziehl Neelse (ZN) stain for Acid Fast Bacilli (AFB) and Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS stain for fungi. Pus swab grew Coagulase negative staphylococcus species, but no fungi. On antibiotic sensitivity, it was sensitive to aztreonam, carbencillin, cefotaxime, cefoxitin, ceftazidime, ofloxacin, piperacillin tazobactum.
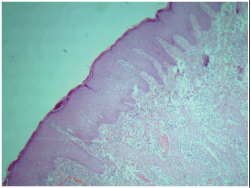
Biopsy was taken from edge of the lesion and showed mild to moderate acanthosis of epidermis with moderate lymphocytic infiltrates in dermis and focally a few neutrophils and histiocytes [Table/Fig-2]. Patient responded to long-term parenteral (intravenous) cefotaxime therapy at the dose of 1gm twice daily for 12 days, simultaneously wet compresses were given to the lesions and curettage was done. The skin lesions started to heal and then the therapy was shifted to oral cefixime 200mg twice daily for 3 weeks. He was also advised on maintaining a healthy diet and good hygiene and to stop alcohol consumption and smoking. Clinico-pathological findings, positive bacterial culture and negative staining for AFB and fungi strongly suggested the diagnosis of blastomycosis-like pyoderma.
Shows moderate acanthosis of epidermis with lymphocytic infiltrate and a few neutrophils in dermis.
Discussion
Blastomycosis like pyoderma, a rare condition manifests as vegetating skin lesions, is an unusual tissue reaction possibly to bacterial infection [1]. In India, there are few case reports of blastomycosis-like pyoderma. It presents as vegetating skin lesions similar to blastomycosis or warty tuberculosis. Staphylococcus aureus, beta-haemolytic streptococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, E-coli and Candida albicans are the most common causative organisms [2]. Factors like alcoholism and nutritional deficiency lead to impairment of host defenses resulting in reduction of skin resistance to bacterial invasion [3]. Other predisposing factors are leukaemia, primary immunodeficiency, immunosuppressive therapy, X-ray irradiation, diabetes mellitus, obesity. The differential diagnosis for this condition includes: North American Blastomycosis, Chromoblastomycosis, Coccidiodomycosis, Phycomycosis, Bromo-derma/Iododerma, Pyoderma gangrenosum [4].
Su, et al., have proposed the criteria for diagnosis of Blastomycosis like pyoderma [4].
Large verrucous plaques with multiple pustules and elevated border.
Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with abscesses in tissue biopsy specimen.
Growth of at least one pathogenic bacterium from the culture of tissue biopsy specimen.
Negative culture for deep fungi, atypical mycobacteria and M.tuberculosis.
Negative fungal serology test result.
Normal bromide and iodide levels in blood.
Systemic antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment. Several treatment modalities have been tried including antibiotics like penicillin, ciprofloxacin, minocycline, cotrimoxazole, focal injection of vancomycin, topical antibiotics, wet compresses and curettage [5]. Recently retinoids and carbon dioxide laser debridement have been tried.
In a case report by Lee et al., despite isolating bacteria, antibiotics were ineffective hence, acitretin was started and the lesions resolved in 3 months [6]. Another case was reported in a 50-year-old female with chronic myeloid leukaemia. She responded to co-trimoxazole within a week [7]. Cecchi et al., reported a case in a 79-year-old female with a recurrent vesicular eczema an her hands since many years. Acitretin, ciprofloxacin and topical clindamycin gel had relieved the symptous of the patient [8].
Conclusion
We present this case for its rarity, as a timely diagnosis is very much important since this condition requires long term anti-biotic therapy and correction of underlying predisposing factors.
[1]. Sawalka S, Phiske M, Jerajani HR, Blastomycosis like pyodermaIJDVL 2007 73:117-19. [Google Scholar]
[2]. Singh M, Kumar B, Kaur S, Malik A, Blastomycosis like pyodermaIJDVL 1985 51:226-28. [Google Scholar]
[3]. Brown CS, Kligman AM, Mycosis like pyodermaArch Dermatol 1957 75:123-25. [Google Scholar]
[4]. Su WP, Duncan SC, Perry HO, Blastomycosis like pyodermaArch Dermatol 1979 115:170-73. [Google Scholar]
[5]. Trygg KJ, Madison KC, Blastomycosis like pyoderma caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Report of a case responsive to ciprofloxacinJ Am Acad Dermatol 1990 23:750-52. [Google Scholar]
[6]. Lee YS, Jung SW, Sim HS, Seo JK, Lee SK, Blastomycosis like pyoderma with good response to acitretinAnn Dermatol 2011 23(3):365 [Google Scholar]
[7]. Duttal TK, James J, Baruah MC, Ratnakar C, Blastomycosis-like pyoderma in a case of chronic myeloid leukaemiaPostgrad Med J 1992 68:363-65. [Google Scholar]
[8]. Cecchi R, Bartoli L, Brunetti L, Pavesi M, Blastomycosis-like pyoderma in association with recurrent vesicular hand eczema: Good response to acitretinDermatol Online J 2011 17(3):9 [Google Scholar]