Gold Tooth Tattoos: Identifying Features in Forensic Odontology
Roma Yadav1, Abhishek Yadav2, Radhika Rai3, Meetika Pahuja4, Savita Solanki5
1 Assistant Professor, Department of Public Health Dentistry, NIMS Dental College, NIMS University, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India.
2 Assistant Professor, Department of Public Health Dentistry, NIMS Dental College, NIMS University, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India.
3 Assistant Professor, Department of Oral Pathology, Faculty of Dental Sciences, SGT University, Gurgaon, Haryana, India.
4 Assistant Professor, Department of Public Health Dentistry, Subharti Dental College, Meerut, Uttar Pradesh India.
5 Assistant Professor, Department of Public Health Dentistry, PDM Dental College, Bahadurgarh, Haryana, India.
NAME, ADDRESS, E-MAIL ID OF THE CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: Dr. Roma Yadav, Assistant Professor, Department of Public Health Dentistry, NIMS Dental College, Shobha Nagar, Jaipur-Delhi Highway, Jaipur-303121, Rajasthan, India.
E-mail: drromayadav@gmail.com
Enamel tattoo, Choumps, Identification
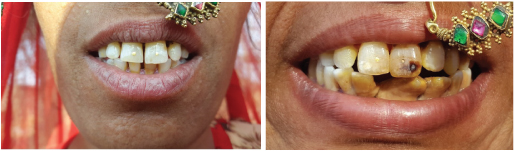
Two females, 39-year-old and 51-year-old reported to the dental checkup camp organized in Kant Kalwar village of Jaipur District by Department of Public Health Dentistry, NIMS Dental College. Both the females came with the chief complaint of dirty teeth. On clinical examination, it was found that they had poor oral hygiene. Apart from periodontal findings, two Gold enamel tattoos were observed on their central incisors (11& 21) [Table/Fig-1&2]. Case history revealed that they had got the gold tattooing done by a tooth tattoo maker in a local fair of their nearby village. They got the enamel tattooing done when they both were teenagers. The purpose of tattooing was to beautify their teeth and they told that their mother and grandmother also had gold tattoos and the custom of getting gold tattoos on front teeth runs in their family.
Clinical pictures showing Gold tattoos on maxillary central incisors.
Discussion
There are different concepts of beauty, based on the traditions, customs and religious rituals set by the ancestors of different communities around the world [1]. Tattooing is a cultural practice or tradition in various civilizations since ancient times. Various forms of tattoos have been practiced by the ancient inhabitants, like tattooing the skin with facial markings of bold lines and dots [2]. Ancient people of southern North America used semi-precious gems to beautify their teeth [3]. Specimens of gold inlays on enamel of central incisors have been found in some parts of China. Even in India, during ancient period of Mahabharata, those who had gold tattoo were considered blessed by the God.
In the present case, Gold had been filled in the cavities prepared with the manual drills on central incisors. This unique kind of practice of gold dental tattoos is practiced in some parts of Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh. These gold tattoos are called enamel choumps and they are mainly placed on the labial surfaces of the maxillary central incisors. Procedure of placing gold tattoo includes the preparation of small circular holes in the tooth enamel by hand drills. Then, small piece of gold wire is hammered into the prepared holes to adapt it properly on the tooth surfaces. These tattoos are made by the local tattoo makers also called as Feruas who come to villages during fairs and festivals. The procedure of making gold tattoo is very unhealthy as they do not sterilize their equipments rather clean them with wet cloth. Gold tattoos are seen among both the sexes but most commonly found in females. In the present case, females belonged to Gujjar tribe where gold tatooing is very commonly practiced. But this practice has also been found in Yaduvanshi, Thakurs & Jaat Tribes of Uttar Pradesh [4].
Besides being a fashion statement (for which they are actually done), tattoos both on the soft and hard tissues have also been used by the forensic odontologists for a more serious cause, that is ‘Identification’. In case of aircraft accidents, explosions, fire and other natural and manmade mass disasters, identification of deceased person becomes very difficult because of mutilated remains or decomposed bodies. So, dental identification plays a primary role and becomes very important to the forensic team, greatly assisting the identification process [5]. Teeth are considered as the hardest structure of the human body and infact, it is said that teeth are the part of a human body most susceptible to disease during a person’s life, yet are the most durable part after a person’s death. This characteristic makes the dentition extremely useful for identification purposes. Even most of the dental restorations including gold inlays and prosthesis remain resistant to the decomposition and destructions even by fires. Historical evidence shows that in 1835 and 1849, the burnt bodies of Countess of Salisbury and Dr. Goerge Parkman, professor in Harvard University were identified by their gold dentures [6]. In such situations anything that distinguishes one person from another, such as prosthetic appliances, dental restorations and dental tattoos, can provide vital clues to forensic odontologists for patient identification.
Teeth displaying highly individual features can aid as valuable adjunctive and can help to a large extent in forensic odontology. Gold enamel choumps prevalent among different tribes and communities can serve as one of the useful tools to forensic odontologists in the identification of deceased person during mass disasters and can prove to be crucial to the successful resolution of forensic investigations.
[1]. Peter T, Titus S, Francis G, Alani MM, George AJ, Ornamental dentistry–an overviewJournal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences 2013 7:666-76. [Google Scholar]
[2]. Mishra P, Gupta M, Shrivastava K, Singh N, Singh P, Oral Tattoos:“Beauty Lies in the Eyes of the Beholder”Advances in Human Biology 2015 2:17-21. [Google Scholar]
[3]. Kim HJ, Karanxha L, Park SJ, Non-destructive management of white spot lesions by using tooth jewelryRestor Dent Endod 2012 37:236-39. [Google Scholar]
[4]. Kotecha SD, Hedge YD, Chaudhry K, Yeluri R, Masih U, Singh C, Gold enamel choumps–a case reportEgyptian Journal of Forensic Sciences 2015 Article in press; Available at (www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2090536X15000428) [Google Scholar]
[5]. Tinoco RL, Martins EC, Daruge E, Daruge E, Prado FB, Caria PH, Dental anomalies and their value in human identification:a case reportJ Forensic Odontostomatol 2010 28:39-43. [Google Scholar]
[6]. Mishra SK, Mahajan H, Sakorikar R, Jain A, Role of prosthodontist in forensic odontology. A literature reviewJ Forensic Dent Sci 2014 6:154-59. [Google Scholar]