Atypical Fibroxanthoma of Scalp: A Paradoxical Benign Tumour
Ritesh Sachdev1, Ruchika Goel2, Smeeta Gajendra3
1 Senior Consultant, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Medanta- the Medicity, Sector 38, Gurgaon, Haryana. India.
2 Consultant, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Medanta- the Medicity, Sector 38, Gurgaon, Haryana. India.
3 Associate Consultant, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Medanta- the Medicity, Sector 38, Gurgaon, Haryana. India.
NAME, ADDRESS, E-MAIL ID OF THE CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: Dr. Ritesh Sachdev, Senior Consultant, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Medanta-The Medicity, Sector – 38, Gurgaon, Haryana-122 001, India.
E-mail: sachdev05@gmail.com
Atypical fibroxanthoma, Cytokeratin, CD68, CD10
Atypical fibroxanthoma (AFX) is a recently described soft tissue tumour by World Health Organization as a benign tumour of uncertain differentiation, occurring on sun exposed skin in elderly individual [1]. The bizarreness as well as marked atypia seen in the cells raises a first impression of malignant tumour, whereas it is rarely so. It has a male predominance (70%) with an average age of presentation of 71.9 years, ranging from 29–91 years [2].
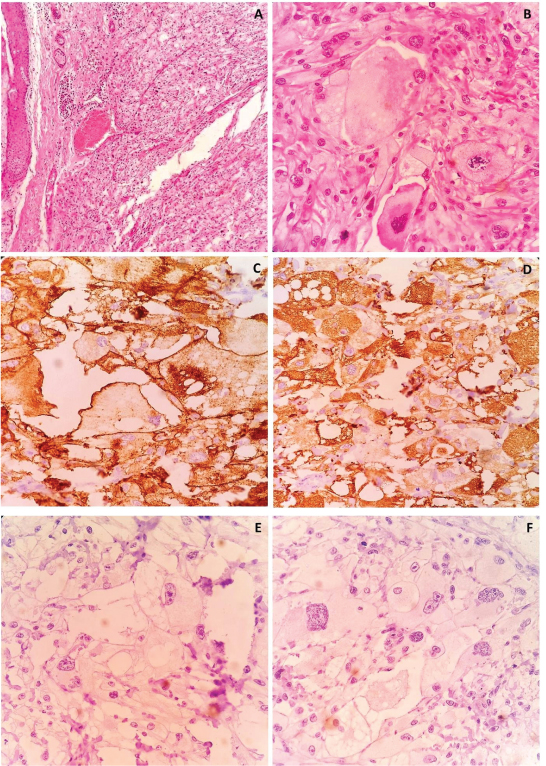
An 81-year-old male presented with hard nodular scalp swelling since 7 to 8 years with a rapid size increase since 3 months. On examination there was a nodulo-ulcerative lesion measuring 5cm x 3cm on scalp with bleeding edges. He did not have any other cutaneous lesion or lymphadenopathy. Excisional biopsy done outside was reported as sebaceous carcinoma. The patient was referred to our hospital for further management. On review of biopsy slides, the tumour cells were spindled, plump to epithelioid with marked pleomorphism, arranged in haphazard, vaguely fascicular or storiform patterns [Table/Fig-1a]. Tumour cells had hyperchromatic and multilobulated bizarre nuclei with scattered multinucleate tumour giant cells. Some cells of the lesion contained vacuolated and lipid-containing cytoplasm similar to xanthoma raising doubts of sebaceous carcinoma, as diagnosed outside [Table/Fig-1b]. On extensive IHC work up, the tumour cells were positive for Vimentin (Dako;V9) [Table/Fig-1c], CD68 (Leica;514H12), CD10 (Dako;56C6) [Table/Fig-1d] and negative for Cytokeratin (Biogenix;AE1+AE3) [Table/Fig-1e], EMA (Dako, E29), SMA (Dako;1A4), S 100 (Dako;IS504), Desmin (Dako;D33), Caldesmon (Dako; H-CD) and HMB 45 (Dako;HMB45) [Table/Fig-1f]. A final diagnosis of atypical fibroxanthoma was made.
Histopathological examination showing large bizarre cells with abundant foamy cytoplasm and atypical mitosis (H&E: a) 100x; b) 400x). Immunohistochemistry showing positivity for Vimentin (c), CD10 (d) and negativity for Cytokeratin (e), HMB45 (f)
Making a diagnosis of atypical fibroxanthoma is challenging and the diagnosis should be made by exclusion of other differential diagnoses after applying the stringent histological criteria and a broad panel of immunostains. Cutaneous carcinomas and melanoma must be ruled out by immunohistochemistry. Absent immunostaining for cytokeratins, S100 and HMB45 in AFX are helpful for excluding sebaceous carcinoma along with squamous cell carcinoma and malignant melanoma. Other differentials are malignant fibrohistiocytoma, atypical Fibrous Histiocytoma /dermatofibroma with monster Cells and pleomorphic fibroma [Table/Fig-2]. By definition, in AFX tumour cells lack expression of S100, cytokeratin, CD34, desmin and h-caldesmon. Previously our case was misdiagnosed as sebaceous carcinoma due to pleomorphism, abundant clear to foamy cytoplasm and bizarre pleomorphic nuclei. CD10 is a useful marker for AFX and is positive in 95%–100% cases of AFX [2]. A histiocytic marker CD 68 is positive in more than half of cases [3]. AFX shows a very good prognosis after surgical excision [4]. Reports of metastasis are very rare, and recurrence is uncommon [5]. Distinction from high grade sarcoma is crucial to prevent inappropriate aggressive therapy.
Differential diagnoses of atypical fibroxanthoma
| Atypicalfibroxanthoma | Malignantfibroushistiocytoma | Atypical FibrousHistiocytoma /Dermatofibromawith Monster Cells | PleomorphicFibroma |
|---|
| Commonly involvesscalp and neck | Commonlyinvolvesextremities | Commonly involvesextremitiesand trunk | Extremitiesand trunk>scalp andneck |
| Usually abuts epidermis(commonly ulcerated)Minimal involvement ofsubcutis. No muscle orvascular invasion | Extension to deepcutaneous tissue,fascia, muscle withvascular invasion | Grey zonebetween lesionand epidermis | Grey zonebetweenlesion andepidermis |
| Have xanthoma cells | Lacks xanthomacells | Lacks xanthomacells | Lacksxanthomacells |
| CD68 positive | CD 68 positive | CD68 negative | CD68negative |
| Mitotic figurenumerous,often atypical | Mitotic figurenumerous,often atypical | Mitotic figure rare | Mitotic figurerare |
[1]. Calonje JE, Brenn T, Komminoth P, Atpical FibroxanthomaWHO Classifications of Tumours of Soft tissue and Bone. Edited by Fletcher CDA, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn PCW, Meertens F 2013 4th editionLyonIARC Press [Google Scholar]
[2]. Mirza B, Weedon D, Atypical fibroxanthoma: a clinicopathological study of 89 casesAustralas J Dermatol 2005 46(4):235-38. [Google Scholar]
[3]. Hultgren TL, DiMaio DJ, Immunohistochemical staining of CD10 in atypical fi broxanthomasJ Cutan Pathol 2007 34(5):415-19. [Google Scholar]
[4]. Hilgers M, Wahl RU, Megahed M, Atypical fibroxanthoma of scalpe: Overview and recent developmentaHautarzt 2014 65(12):1008-10. [Google Scholar]
[5]. Lee SS, Lewis JM, Liaw K, Bushkell LL, Young YD, Googe PB, Recurrent atypical fibroxanthoma with satellite metastasisJ Cutan Pathol 2015 42(1):56-60. [Google Scholar]