Primary Ewings Sarcoma of the Lung
Kunal K Deokar1, Nana G Kunjir2, Shivhari Ghorpade3
1 Assistant Professor, Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Lokmanya Tilak Municipal Medical College, Sion, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
2 Resident, Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Apollo Hospitals, Chennai, Tamilnadu, India.
3 Professor and Head, Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Govt Medical College, Nagpur, Maharashtra, India.
NAME, ADDRESS, E-MAIL ID OF THE CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: Dr. Kunal K Deokar, 203, Madhuri CHS, Oppsite Prem Nagar, Old Mumbai-Pune Road, Kharegaon, Kalwa, Thane -400605, India. E-mail : dkunal@live.in
Extraosseous ewings sarcoma is an extremely rare neuroectodermal tumour. We report the case of a 30-year-old female who presented with right sided pulmonary mass. Radiology, histopathology and immunohistochemistry confirmed the diagnosis of primary pulmonary Ewings sarcoma. This case highlights the fact that Ewings sarcoma should be considered in differential diagnosis of patients presenting with pulmonary mass.
Extraosseous, Ewings sarcoma, Lung
Case Report
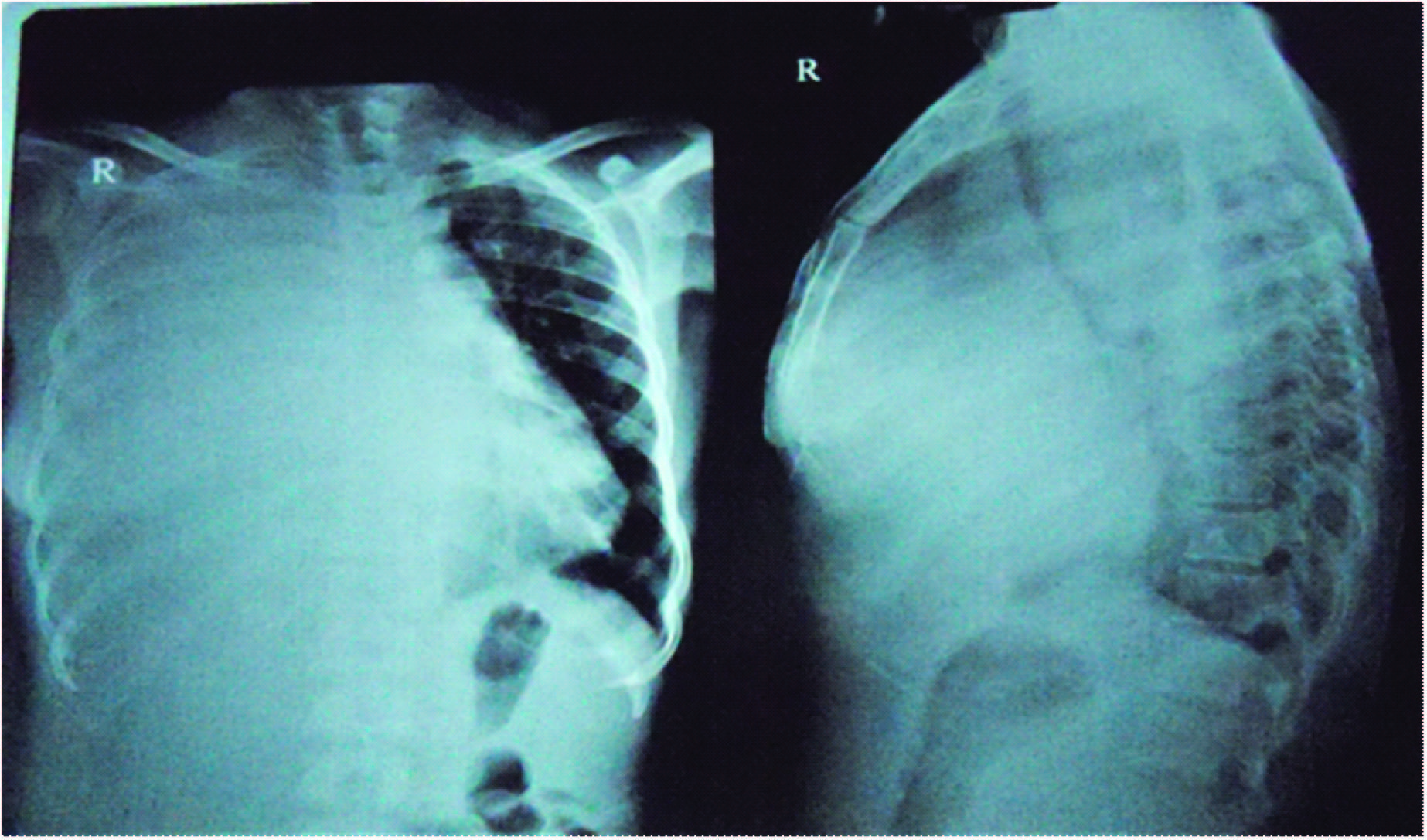
A 30-year-old female was admitted with complaints of right sided chest pain, shortness of breath and cough with scanty white expectoration since three months. Respiratory system examination was suggestive of right sided massive pleural effusion with shift of mediastinum to the left. Chest radiograph PA and lateral view [Table/Fig-1] were suggestive of right sided pleural effusion. Computed tomography (CT) of the chest and abdomen [Table/Fig-2] revealed a large, relatively well-defined, moderately heterogeneously enhancing mass lesion involving right hemithorax with pleural deposits, bilateral axillary nodes and gross right pleural effusion.
Radiograph of the chest PA view showing massive right sided pleural effusion
Computed tomography of the chest showing large, relatively well-defined, moderately heterogeneously enhancing mass lesion involving right hemithorax

The patient underwent CT guided needle biopsy, which revealed small round cells with scanty cytoplasm, round to oval nuclei, fine granular to vesicular chromatin suggestive of malignant small round cell tumour. Immunohistochemical staining for pancytokeratin and CD 45 were negative. The tumour was MIC-2 positive. Thus, the histological and immunohistochemical findings were compatible with Ewings sarcoma [Table/Fig-3a-d]. The patient thereafter underwent PET scan, which did not reveal any evidence of an occult primary. Thus, a definitive diagnosis of primary Ewing sarcoma of the lung with nodal metastasis was made. She was started on chemotherapy but unfortunately the patient died after 15 d.
a) Ewings sarcoma as monotonous sheet of small round cells (Hematoxylin and eosin, original magnification 10×). b) Tumour immunoreactive for Mic-2. c] Tumour negative for CD45. d] Tumour negative for Pancytokeratin

Discussion
Ewings sarcomas are relatively rare neuroectodermal tumours that primarily arise from the bone [1]. Extraosseous ewings sarcomas have been reported but are extremely rare. It was first described in 1921 by James Ewing as an endothelioma of bone [2]. They are neuroectodermal tumours, which primarily arise in the bones and are the second most common primary bone tumour [1]. Translocation t (11, 22) (q24; q12) is pathognomonic of Ewing sarcoma, occurs in 85% of patients and it gives rise to the formation of the EWS-FLI 1 fusion gene [3].
Extraosseous ewings sarcoma is extremely rare. We reviewed the literature using the search terms “Primary Ewings sarcoma lung” and found that only 16 cases have been reported so far. The first case was reported by Hammer et al., [4]. As per previous case reports, the patients were in the age group of 4- 67 y and 10 of the 16 cases were males [Table/Fig-4].
Cases of primary pulmonary ewings sarcoma reported so far
| Author | Year | Age | Sex | Presentation | Treatment | Follow up | Remarks |
|---|
| Hammer et al., [4] | 1989 | 64 | Male | - | Chemo+ Surg + Radiotherapy | - | - |
| Catalan et al., [5] | 1997 | 29 | Male | - | Chemo+Surgery | - | - |
| Tsuji et al., [6] | 1998 | 25 | Female | Intrapulmonary mass | Surgery | Death after 2y | No evidence of extrapulmonary involvement by the tumour at presentation |
| Tsuji et al., [6] | 1998 | 15 | Male | Intrapulmonary mass | Chemo+Surgery | No evidence of recurrence for 2 y | No evidence of extrapulmonary involvement by the tumour at presentation. |
| Imamura et al., [7] | 2000 | 41 | Male | Tumour in the left upper lung | Chemo+Surgery | No recurrence after 22 mnth | - |
| Imamura et al., [7] | 2000 | 30 | Female | Tumour in the right lower lung | Chemo+Surgery | No recurrence after 16 mnth | - |
| Kahn et al., [8] | 2001 | 18 | Male | Right middle lobe mass | Surgery (Right Middle lobectomy) | Death after 2y | 2 years after surgery, there was local recurrence for which patient underwent right upper and lower lobectomy |
| Mikami et al., [9] | 2001 | 17 | Female | Right lower lobe mass | Chemo +Surg + Radiotherapy | Death after 3mts | Metastases in mediastinum and right thoracic wall detected 3 months after surgery |
| Takahashi et al., [10] | 2006 | 8 | Male | Right upper | Chemo+Surgery | No recurrence for 9 mts after surgery | - |
| Young Lee et al., [11] | 2007 | 67 | Male | Left lower lobe mass | Surgery +Chemo | - | No evidence of metastases at presentation |
| Antelo et al., [12] | 2009 | 22 | Female | Right lower zone mass | Chemotherapy | - | No evidence of metastases at presentation |
| Hancorn et al., [13] | 2010 | 44 | Male | Right upper lobe mass | Surgery | - | Was found to have cerebral metastases 5 weeks following surgery |
| Siddiqui et al., [14] | 2011 | 15 | Female | Mass involving entire right hemithorax | Chemotherapy + radiotherapy | Died after 8 mnth | Metastatic nodule in the left lower lobe |
| Ichiki et al., [15] | 2012 | 42 | Male | Right lower lobe mass | Surgery + chemotherapy | No recur ence for 6 mnth after surgery | - |
| Alsit et al., [16] | 2013 | 4 | Female | Left upper Zone mass | Surgery + chemotherapy | - | - |
| Andrei et al., [17] | 2013 | 31 | Male | Mass in the lingual of left lung | Surgery +Chemotherapy + Local radiationtherapy | - | - |
| Present case | - | 30 | Female | Mass involving entire right hemithorax | Chemotherapy | Died | - |
Histologically, the tumour consists of a proliferation of small round cells with scanty and clear cytoplasm, round to oval nuclei, finely granular chromatin, and inconspicuous nucleoli. It is Periodic acid schiff positive due to the presence of cytoplasmic glycogen. Histologic differential diagnoses include small cell carcinoma, malignant lymphoma, alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, neuroblastoma. Tumours have a strong reactivity to CD99/MIC-2 and vimentin. In some cases, they may be positive for markers of neural differentiation like S-100, neuron specific enolase and 20% of cases are positive for cytokeratins. Demonstration of translocation t (11, 22) (q24; q12) by fluorescent insitu hybridisation (FISH) and/or reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is used to support the diagnosis [1].
Due to its rarity, there are no specific guidelines for the treatment of this disease. The treatment should be aggressive and should consist of surgery followed by chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Conclusion
We have described an extremely rare case of primary pulmonary ewings sarcoma. Though rare, it should be considered in the differential diagnosis of children and adults presenting with primary pulmonary mass.
[1]. Bernstein Mark, Kovar Heinrich, Paulussen Michael, Ewing's sarcoma family of tumours: Current managementThe Oncologist 2006 11:503-19. [Google Scholar]
[2]. Ewing J, Classics in oncology. Diffuse endothelioma of bone. Proceedings of the New York Pathological Society, 1921CA Cancer J Clin 1972 22:95-98. [Google Scholar]
[3]. Turc-Carel C, Aurias A, Mugneret F, Chromosomes in Ewing's sarcoma. An evaluation of 85 cases of remarkable consistency of t (11; 22) (q24; q12)Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1988 32:229-38. [Google Scholar]
[4]. Hammar S, Bockus D, Remington F, Cooper L, The unusual spectrum of neuroendocrine lung neoplasmsUltrastruct Pathol 1989 13:515-60. [Google Scholar]
[5]. Catalan RL, Murphy T, Primary primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the lungAm J Roentgenol 1997 169:1201-02. [Google Scholar]
[6]. Tsuji S, Hisaoka M, Morimitsu Y, Hashimoto H, Jimi A, Watanabe J, Peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumour of the lung: report of two casesHistopathology 1998 33:369-74. [Google Scholar]
[7]. Imamura F, Funakoshi T, Nakamura S, Mano M, Kodama K, Horai T, Primary primitive neuroectodermal tumour of the lung: report of two casesLung Cancer 2000 27:55-60. [Google Scholar]
[8]. Andrea G, Kahn, Alejandra Avagnina, Jorge Nazar, and Boris Elsner. Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumour of the LungArchives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine 2001 125(3):397-99. [Google Scholar]
[9]. Mikami Y, Nakajima M, Hashimoto H, Irei I, Matsushima T, Kawabata S, Primary pulmonary primitive neuroectodermal tumour (PNET): A case reportPathol Research and Practice 2001 197:113-39. [Google Scholar]
[10]. Takahashi Daijiro, Nagayama Jun, Nagatoshi Yoshihisa, Primary ewing’s sarcoma family tumours of the lung – a case report and review of the literatureJpn J Clin Oncol 2007 37(11):874-77. [Google Scholar]
[11]. Lee Yoon Young, Kim Do Hoon, Lee Ji Hye, Primary pulmonary ewing's sarcoma/Primitive neuroectodermal tumour in a 67-year-old manJ Korean Med. Sci 2007 22(Suppl):S159-63. [Google Scholar]
[12]. Juan Suárez Antelo, Carlota Rodríguez García, Carmen Montero Martínez, Héctor Verea Hernando, Pulmonary ewing sarcoma/Primitive neuroectodermal tumour: A case report and a review of the literatureArchivos De Bronconeu-mologia 2010 46(1):44-46. [Google Scholar]
[13]. Kate Hancorn, Anita Sharmab, Michael Shackcloth, Primary extraskeletal Ewing’s sarcoma of the lungInteractive Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery 2010 :803-04. [Google Scholar]
[14]. Siddiqui Mohammed Azfar, Akhtar Jamal, Shameem Mohammad, Baneen Ummul, Zaheer Samreen, Shahid Mohammad, Giant extraosseous Ewing sarcoma of the lung in a young adolescent female – A case reportActa Orthop Belg 2011 77:270-73. [Google Scholar]
[15]. Yoshinobu Ichiki, Akira Nagashima, Yasuhiro Chikaishi, Manabu Yasuda, Ichiro Yamamoto, Satoshi Toyoshima, Primary pulmonary ewings sarcoma: report of a caseSurg Today 2012 42:812-15. [Google Scholar]
[16]. Nidal Alsit, Clara Fernandez, Jean Luc Michel, Linda Sakhri, Audrey Derouet, Augustin Pirvu, Primary extraosseous Ewing sarcoma of the lung in childrenE Cancer 2013 7:312 [Google Scholar]
[17]. Mirela Andrei, Stewart F Cramer, Zachary B Kramer, Amer Zeidan, Bishoy Faltas, Adult primary pulmonary primitive neuroectodermal tumour: Molecular features and translational opportunitiesCancer Biology and Therapy 2013 14(2):75-80. [Google Scholar]