Prosthodontic Management of Flat Mandibular Ridge by Mini Implant Supported Over Denture
Mirna Garhnayak1, Lokanath Garhnayak2, Shruti Dev3, Aswini Kumar Kar4, Abhijita Mohapatra5
1Reader, Department of Prosthodontics, Institute of Dental Sciences & Hospital, S.O.A. University, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India.
2Assistant Professor, Department of Prosthodontics, S.C.B. Dental College & Hospital, Cuttack, Odisha, India.
3Professor, Department of Prosthodontics, Kalinga Institute of Dental Sciences, Campus-5, KIIT University, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India.
4Reader, Department of Prosthodontics, Kalinga Institute of Dental Sciences, Campus-5, KIIT University, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India.
5Reader, Department of Prosthodontics, Kalinga Institute of Dental Sciences, Campus-5, KIIT University, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India.
NAME, ADDRESS, E-MAIL ID OF THE CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: Dr. Mirna Garhnayak, Reader, Prosthodontics, Institute of Dental Sciences & Hospital, S.O.A. University, Bhubaneswar, Odisha-751003, India.
Phone: 8457011217, 8763499135
E-mail: mirnagarhnayak@gmail.com
Loosening of lower denture has always been a common complaint of denture wearer, particularly in case of severe bone resorption. Various treatment modalities including preprosthetic surgery or ridge augmentation therapy to improve the ridge height and conventional implant treatments are available. But many patients are not willing to undergo through such extensive surgical procedure or conventional twin stage implant therapy owing to the chronic old age ailment and cost factor. So mini implant (SENDAX MDI) supported over denture is a boon for them who want a quick and minimally invasive solution, with a much lower cost. In this article we shall discuss the case report of a 60-year-old female patient with atropic mandibular ridge rehabilitated with MDI, (mini dental implant), Sendax mini implant.
MDI, Mini dental implant, Over denture, Sendax mini implant
Case Report
A 60-year-old female patient reported to the clinic, with the chief complaints of loose lower denture and difficulty in chewing for which she inquired about fixed denture.
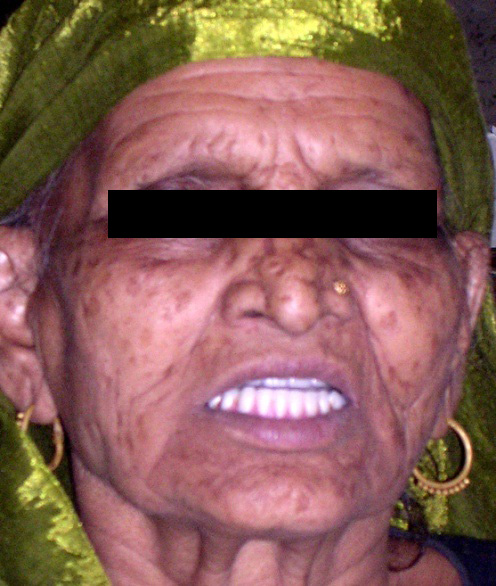
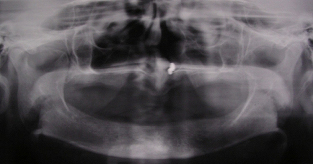
Her medical history was not suggestive of any known systemic disease. She had been using her existing set of denture for the past two months. Intra oral examination revealed completely edentulous maxillary and mandibular ridges with the later being moderately resorbed with ill fitted lower denture [Table/Fig-1]. On radiographic examination, [Table/Fig-2] the bone quality was found to be Type II in the mandibular anterior region [1] . The height and width of the bone were inadequate to receive the standard diameter implants [1] .As the upper denture was quite retentive with satisfactory occlusion of the existing denture, it was decided to stabilize the mandibular denture with four MDI implants & treatment plan was discussed with the patient.
Patient with ill fitted lower denture
Surgical splint with guiding holes
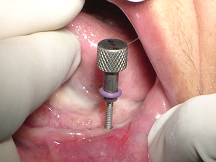
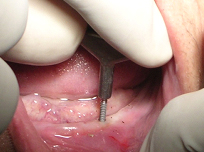
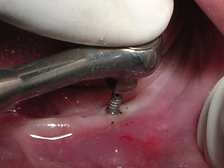
All four implants in place
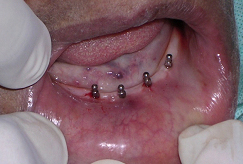
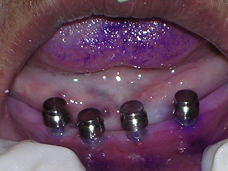
‘0’ Ring housing placed over implants
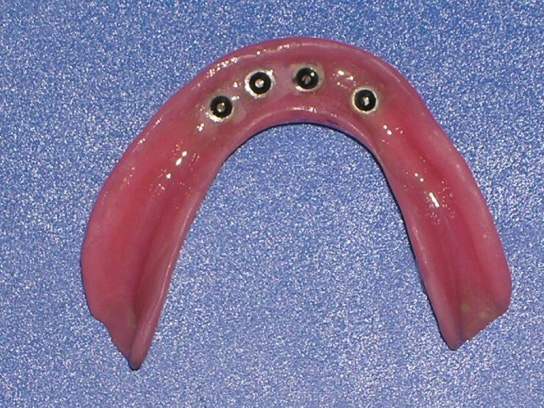
Relieved area of lower denture corresponding to ‘0’ ring housing
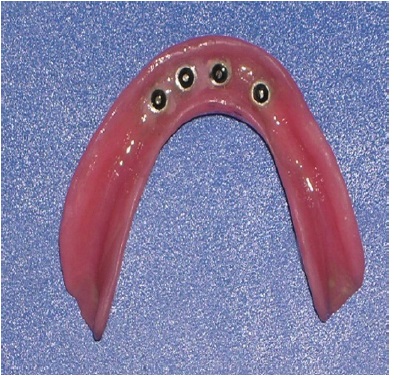
‘0’ Ring housing transferred to lower denture
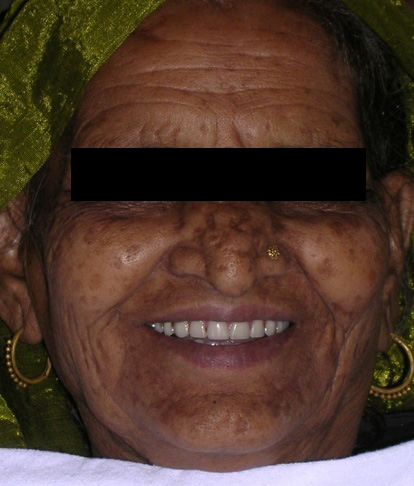
Implant supported lower denture in place
Procedure
A surgical guide splint made up of clear auto polymerizing acrylic resin (DPI-RR; Dental Products of India Ltd, Mumbai, India) was fabricated. After tissue asepsis and infiltration anaesthesia, transgingival implantation (2Nos.13mmx1.8mm & 2Nos 10mmx1.8mm) was performed using the surgical splint in the canine & first bicuspid region posteriorly and lateral incisor anteriorly [Table/Fig-3] [2].
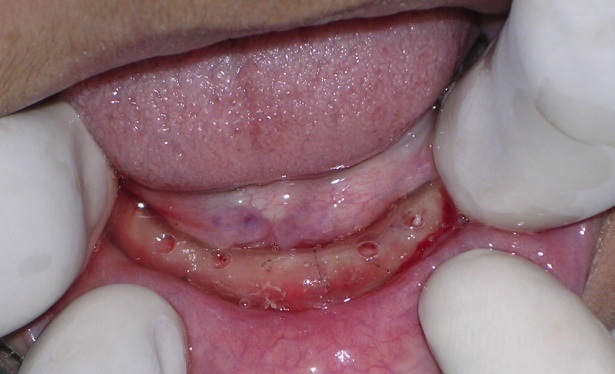
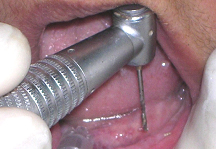
A pilot hole was prepared to a depth of 1/2 to 2/3rd of implant length with the help of a pilot drill (1.1mm diameter) in a tapping motion using copious irrigation [Table/Fig-4]. The implants were screwed into the pilot holes with the help of finger driver, winged and ratchet wrench respectively [Table/Fig-5a,5b,5c]. The self tapping and cutting features of the implants facilitated their complete insertion, which helped in their immediate loading due to instant stabilization [3]. It was ensured that no threads of implants were supra gingival except 1-1.5mm of square neck portion [Table/Fig-6]. A distance of 10mm was maintained between the implants. The next step was attachment of O-ring into the tissue surface of existing lower denture. For this, the O-ring housings were placed on the implant O-ball and the corresponding areas on the denture were adequately relieved with a carbide bur[Table/Fig-7a,7b]. A chair side relining was carried out for this attachment [Table/Fig-8].
The patient was advised to wear the denture continuously for 24 hours to prevent any swelling. Recall appointments were scheduled at 24hours, 3 days and 1week respectively [4] with proper oral hygiene care. She was highly satisfied with the improved stability of the denture and was able to chew food soon after surgery [Table/Fig-9].
Discussion
Edentulism secondary to loss of teeth is a chronic condition and the therapy is palliative aimed at improving functional quality of life [3]. Though complete denture treatment has catered to these needs to some extent, rehabilitation of atrophic mandibular ridge is still a challenge in terms of patient satisfaction [5]. A common complaint is inability to chew food because of loose lower denture which in turn leads to poor nutrition and affect the well being of patient [6].
The common factors responsible for the maladapted lower complete dentures are decreased vestibular depth and denture bearing area, [7] narrow (<5mm) and atrophic ridge etc. An inadequate bone volume makes it difficult for denture to be stabilized by conventional standard diameter implants (3.5mm & wider) without ridge augmentation [8]. Moreover, few patients opt for this because of multiple surgical procedure and cost factors. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), USA approved Mini Dental Implant (MDI) supported overdentures which are better alternatives in such cases as they are minimally invasive with single stage surgical procedure where denture can be loaded immediately [1,9] These implants are affordable and patient satisfaction is excellent too [10].
In the present case use of single piece implant makes the restorative phase simple and cost effective. The ridge was of narrow width, height of bone was less and of Type I/II variety [11]. So total of four implants (13mm length × 1.8mm diameter) were used as they have the same BIC (bone-implant contact) as of two standard implants [12] and the arch distribution of multiple MDI better offset any fulcrum or tipping effect that can occur with two conventional implant positioned at canine area [13]. Despite narrow diameter, they have sufficient pullout strength as the later is dependent on length rather than diameter [14]. The auto advancement thread pattern allows the implant to be immediately loaded as it creates a stable, compacted 20bone interface rather than bone healing towards the implant from a conventional osteotomy side [14]. A standard thread design was used as the bone was of Type I/II variety. These designs help in initial contact, improves initial stability, enlarge surface area and give the implant favourable dissipation force. The micro rough surface is conducive to the osseointegration [15]. Additionally, Kanie et al., compared the mechanical properties of mini transitional implant (MTI, Dentatus USA, New York, NY) and the MDI (IMTEC) [15]. They found that the MDI is stronger and more likely to integrate making it suitable for longterm use[15]. Long term success of these implants have also been supported by few other studies [10,12,16].The simple surgical and prosthetic procedure make it easy and learnable even for the general practioner. There was no marked difference in satisfaction between subjects with ball and socket and bar-clip retained two implant mandibular overdentures at initial evaluation and after 10-years of function [17]. Clinical parameters revealed healthy mucosal conditions and stable marginal bone levels, determined radiographically. However, probing depths around implants provided with ball and socket attachments were slightly shallower than those with bar-clip attachments after 10-years of function [17]. Chances of damaging the inferior alveolar nerve is less here as the implants are placed anterior to the mental foramina. These implants can also be used in case of medically compromised patients and when patients have financial constraint for conventional implants [10]. Proper care should be taken to avoid some potential complications like implant breaking due to insufficient instrumentation of the pilot opening. On the contrary over instrumentation should be avoided as it causes loss of stability. If an implant lacks initial stability, it should not be loaded immediately and the corresponding area should be covered with tissue conditioner till it is stabilized [18]. To avoid the possible lingual piercing of the denture during the O-ring housing fixation, lingual portion of the denture should be thickened intentionally with the heat polymerised acrylic resin.
Conclusion
Providing a stable immediate functional aesthetic to the patient has been the main objective of every dentist. It has come as a boon for the medically compromised and elderly patient with resorbed ridge because of its low cost and minimal surgical procedure. The simple surgical and prosthetic procedure with minimal complication also make it easy and learnable even for the general practioners.
[1]. TE Shatkin, S Shatkin, AJ Oppenheimer, Mini dental implants for the general dentist: a novel technical approach for small-diameter implant placementCompendium. 2003 24:26-34. [Google Scholar]
[2]. H Simon, AA Caputo, Removal torque of immediately loaded transitional endosseous implants in human subjectsInt J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2002 17:839-45. [Google Scholar]
[3]. BE Balkin, DE Steflik, F Naval, Mini-dental implant insertion with the autoadvance technique for ongoing applicationsJ Oral Implantol 2001 27:32-37. [Google Scholar]
[4]. JN Walton, MI MacEntee, A retrospective study on the maintenance and repair of implant-supported prostheses 1993 6(5):451-55. [Google Scholar]
[5]. GA Zarb, Osseointegration: On Continuing Synergies in Surgery, Prosthodontics, Biomaterials 2008 ChicagoQuintessence Publishing Co:4-13. [Google Scholar]
[6]. JG Steele, National diet and nutrition survey people aged 65 years and over. Vol 2: Report of the oral health survey 1998 London, UKThe Stationary Office [Google Scholar]
[7]. A Tallgren, The continuing reduction of the residual alveolar ridges in complete denture wearers: a mixed-longitudinal study covering 25 yearsJ Prosthet Dent 1972 27(2):120-32. [Google Scholar]
[8]. GJ Christensen, The increased use of small-diameter implantsJ Am Dent Assoc 2009 140(6):709-12. [Google Scholar]
[9]. MR Ahn, KM An, JH Choi, DS Sohn, Immediate loading with mini dental implants in the fully edentulous mandible.Implant Dent 2004 13(4):367-72. [Google Scholar]
[10]. TM Griffitts, CP Collins, PC Collins, Mini dental implants: An adjunct for retention, stability, and comfort for the edentulous patientOral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2005 100(5):e81-4. [Google Scholar]
[11]. RB Summers, A new concept in maxillary implant surgery : The osteotome technique.Compend Contin Educ Dent 1994 15(2):152-60. [Google Scholar]
[12]. H Lerner, Minimal invasive implantology with small diameter implantsImplant Pract. 2009 2(1):30-5. [Google Scholar]
[13]. CE Englsh, GC Bohle, . Diagnostic, procedural, and clinical issues with the Sendax mini dental implants.Compendium. 2003 24(1):1-23. [Google Scholar]
[14]. MS Block, A Delgado, MG Fontenot, The effect of diameter and length of hydroxyapatite-coated dental implants on ultimate pullout force in dog alveolar boneJ Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1990 48(2):174-8. [Google Scholar]
[15]. T Kanie, M Nagata, S Ban, Comparison of the mechanical properties of two prosthetic mini-implants.Implant Dent. 2004 13(3):251-6. [Google Scholar]
[16]. RA Bulard, JB Vance, Multi-clinic evaluation using mini-dental implants for longterm denture stabilization: A preliminary biometric evaluationCompend Contin Educ Dent. 2005 26(12):892-7. [Google Scholar]
[17]. M Cune, M Burgers, F van Kumpen, C de Putter, A van der Bilt, Mandibular overdentures retained by two implants : 10 years results from a crossover clinical trial comprising ball-socket and bar-clip attachments.IJP. 2010 23(4):310-7. [Google Scholar]
[18]. PJ Henry, GJ Liddelow, Immediate loading of dental implantsAust Dent J. 2008 53(1):69-81. [Google Scholar]