Conjoined Twins: A Rare Case of Thoraco-Omphalopagus
Ankur Aneja1, Dayananda Kumar Rajanna2, Vikram Narasimha Reddy3, Kamala Retnam Mayilvavaganan4, Poornima Pujar5
1 Junior Resident, Department of Radiodiagnosis and Modern Imaging, MV Jayaram Medical College and Research Hospital, Bangalore-562114, India.
2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis and Modern Imaging, MV Jayaram Medical College and Research Hospital, Bangalore-562114, India.
3 Junior Resident, Department of Radiodiagnosis and Modern Imaging, MV Jayaram Medical College and Research Hospital, Bangalore-562114, India.
4 Junior Resident, Department of Radiodiagnosis and Modern Imaging, MV Jayaram Medical College and Research Hospital, Bangalore-562114, India.
5 Junior Resident, Department of Radiodiagnosis and Modern Imaging, MV Jayaram Medical College and Research Hospital, Bangalore-562114, India.
Name, Address, E-Mail Id of The Corresponding Author: Dr Ankur Aneja, D II / 357, Pandara Road, New Delhi-110003, India.
Phone: 09538560349
E-mail: doc.ankur.aneja@gmail.com
Conjoined twins are a rare entity. Only few cases have been reported in the medical literature. They are a rare and exclusive type of monozygotic twins. They are caused by a faulty division of the embryonic disk. Due to high post-natal morbidity and mortality, an early pre-natal diagnosis is a must. All the monozygotic twins should be carefully screened for conjoinnment and if it is present, the type and the degree of sharing of the foetal organs should be delineated. There are many associated anomalies, of which congenital heart defects are the major prognostic factors. Here, we are reporting a case of thoraco-omphalopagus in which there was sharing of the foetal heart, liver and the intestinal loops.
Embryonic disk, Monozygosity, Thoracopagus, Omphalopagus
Case Report
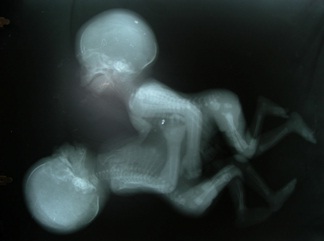
A 25 years old multigravida presented with amenorrhoea of twenty four weeks, for a routine antenatal sonological examination, who had a past history of one medical termination of pregnancy and two full term vaginal deliveries. She had her last delivery three years back. There was no family history of twins. On sonological examination, an evidence of twins could be seen, without an intervening septa, a single anterior placenta, Brenner’s grade II and normal amniotic fluid [Table/Fig-1]. The twins shared a common heart with communication between the ventricles of both the hearts [Table/Fig-2]. There was a common liver and common intestinal loops [Table/Fig-3]. Post natally, a radiograph was obtained, which showed that the twins were connected at the lower chest and at the upper abdomen, upto the umbilicus. All the four limbs were separate and there was no evidence of other significant congenital anomalies [Table/Fig-4]. Postnatally, the babies had an Apgar score of 0/10; both were males, which is unusual for conjoined twins. Both died immediately. The babies had a fused lower chest and an anterior abdominal wall up to the umbilicus. No craniofacial or spinal anomalies were noted on prenatal ultrasound.
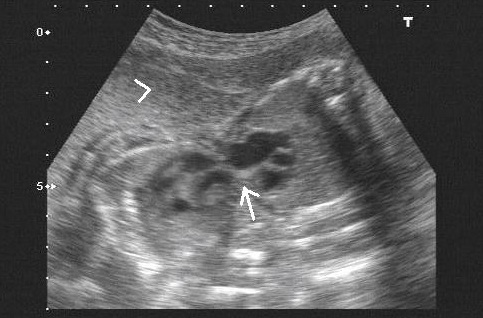
Transverse section at the level of four chambers of heart showing communication between ventricles of both fetal hearts (arrow), placenta is situated anteriorly (arrowhead)
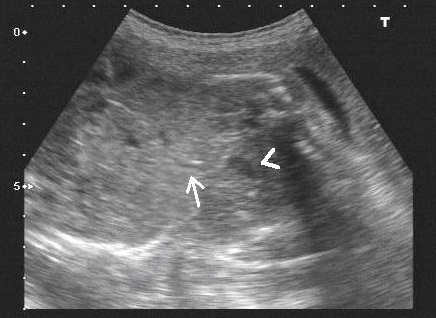
Transverse section at the level of stomach bubble (arrowhead) showing conjoined liver
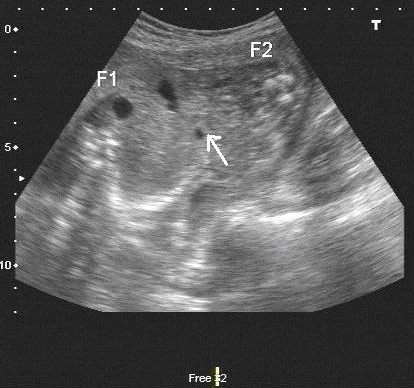
Transverse section at the level of midabdomen showing conjoined intestinal loops (arrow)
Post natal radiograph showing fused lower chest and upper abdomen
Discussion
The first case of conjoined twins on USG was reported in 1976 [1]. Conjoined twins are a rare form of monozygotic twins. The incidence of these babies is one in fifty thousand to one in one lakh pregnancies [2]. The frequency of congenital twins is independent of the maternal age and the parity and it is mostly sporadic. The earliest reported case of Thoracopagus in the literature was reported in the seventh week of pregnancy [3]. Conjoined twins are usually females, which is interesting, as a majority of the monozygotic twins are males. Polyhydramnios is frequently present. Embryologically, conjoined twins occur only in monozygotic twins. If division of the embryonic disk occurs thirteen days after the fertilization and is incomplete, conjoined twins will result. There are two different theories that explain the formation of conjoined twins. According to the “Fission theory”, 13-15 days after fertilization, the embryonic disc undergoes an incomplete separation, whereas in the “Fusion theory”, two separate monoovulatary embryonic discs undergo a secondary association. Recently the “Fusion theory” has been accepted, because it can explain all the conjoined twin phenomena [4]. There are five types: Thoracopagus, Omphalopagus, Pygopagus, Ischiopagus and Craniopagus. With an incidence of 74-75%, Thoracopgus is the most common variety with an incidence of 0.5%. Omphalopagus is the least common variety. Ultrasonography is the most accurate technique which can be used for its diagnosis. In the earlier weeks, the foetal movements are limited and the monochorionic twins may be mistaken for conjoined twins. Hence, a repeat scanning should be done in the eleventh and twelveth weeks of the gestation, to confirm the diagnosis [5]. The other abnormalities which should be looked for in conjoined twins are neural tube defects, orofacial defects, an imperforate anus and diaphragmatic hernia. Associated congenital heart abnormalities are the major prognostic factors for the survival [6].
Conclusion
If they are diagnosed before viability, the parents should be offered termination of the pregnancy. A vaginal delivery is reserved for the stillbirths and for those twins who do not survive [7]. Most of them deliver preterm. 40% of them stillbirths and 35% die within 24 hours [7]. In thoracopagus, the degree of fusion of the heart determines the outcome [8]. In the order of the frequency, the pygopagus twins fare better than the omphalopagus and the thoracopagus twins.
[1]. Wilson RL, Cetrulo CL, Shaub MS, The prepartum diagnosis of conjoined twins by use of diagnostic ultra soundAm. J. of Obstet and Gynecol 1976 126(6):737 [Google Scholar]
[2]. Hanson JW, Incidence of conjoined twinsLancet 1975 2:1257 [Google Scholar]
[3]. Taner MZ, Kurdoglu M, Taskiran C, Kurdoglu Z, Himmetoglu O, Balci S, Early prenatal diagnosis of conjoined twins at 7 weeks 6 days gestation with two dimensional ultrasound: a case reportCases J 2009 2:8330 [Google Scholar]
[4]. Spencer R, Theoretical and analytical embryology of conjoined twins. Part I: EmbryogenesisClinical Anat 2000 13:36-53. [Google Scholar]
[5]. Pajkrt E, Jauniaux E, First trimester diagnosis of conjoined twinsPrenat Diagn 2005 25:820-6. [Google Scholar]
[6]. Chen CP, Thoraco-omphalopagus twins associated with omphalocoele and an umbilical cord cystTaiwan J Obstet Gynecol 2007 46:183-4. [Google Scholar]
[7]. Sakala EP, Obstetric management of conjoined twins Obstet Gynecol 1986 67:21-25. [Google Scholar]
[8]. Razavi-encha F, Mulliez N, Benhaiem-Sigaux N, Cardiovascular abnormalities in thoracopagus twins. Embryological interpretation and reviewEarly human development 1987 15(1):33-34. [Google Scholar]