Introduction
People with a doctorate title in medieval Europe were authorised to teach the high-ranked clerics, church fathers, and other Christian authorities. People holding such a title who were all Catholics were engaged in teaching and interpreting the Bible. Only they were allowed to test others for a “pledge of loyalty”. In 1213, lastly, the Pope granted a PhD license to the University of Paris and later became Licentia ubiquie docendi as a “universal license to teach”. In the 13th century, the titles of academic degrees were Scholar, Bachelor and Master [1].
To obtain a better degree and a higher prestige, the Magister and the Doctorate stages were introduced, serving as a particular attestation and certification to teach at university. By 1785, women had no right to study at doctorate programs. The first woman to receive this degree was “Maria Isidra de guzman yde la cerda” [2]. However, the Universities of Oxford and Cambridge refused to admit female doctoral students until 1920 and 1926, respectively. The title of PhD was first created in the United States from the combination of the traditional British Bachelor of Science (BSc), Master of Science (MSc), and the reforms that took place in the research study of Germany, in 1900. Then, it has been used in Canada and England. Since universities turned toward research-based (and not teacher-centered) education, the importance of doctoral degrees got further increased [3,4].
Usually, a PhD degree consists of specialised work and is granted a dissertation consisting of about 80,000 to 100,000 words. Such a degree is awarded to qualified individuals by universities in many countries. Everyone who has been awarded this degree can teach at the college level in their own field of specialty or work in that particular profession. There are several types of doctorate, the most commonly of which is called PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) [5].
In advanced countries, having a PhD degree is not required for taking a faculty membership or serving as the head of a department. The most important requirements for obtaining a PhD degree are research and teaching abilities. In these countries, the nature of the PhD degree is different for presenting the content. In general, a PhD degree has been created in a certain area for the acquisition of the necessary skills [6,7].
People have different motivations to complete a PhD program. A PhD candidate may run into several questions that need to be answered: What are the types of doctorate programs? What are the pros and cons for going through a doctorate program? What are the possible benefits of holding a doctorate program? Is there generally a need for educating people with PhD degrees in a society? The problems faced by a person during the course, the status of PhD graduates, their employment, and the structure of the PhD programs in different countries are discussed in this study. To address these issues, the present narrative review focuses on the status and challenges of Doctoral programs in the world with special attention to Iran.
Type of Doctorates
There are several types of doctorate which are presented in brief in [Table/Fig-1] and in the future, much will be added to cover more specialties [8,9].
Shows different doctorate programs offered at the present time [8,9].
| Type of PhD program | Definition/Requirements | Subjects and Type |
|---|
| PhD in Education and Research | Facilitating the research and fascinating the access to its product (a Doctoral degree by dissertation or PhD by Research) | AllAcademic and Professional |
| Excellent doctorate | Publishing a series of own specialised research in reputable journals | Academic |
| Honorary doctorate | Doing a great job at the university or the community level | AllAcademic and Professional |
| The highest-rank PhD | Having the best scientific work in modern society | AllAcademic |
| PhD by publication | Having an original contribution to a particular field of study | Academic |
Objectives, Necessities, and Benefits of Holding PhD Programs
Postgraduate education at the PhD level has many benefits for the community, some of which are outlined below [10]:
Offering and holding PhD courses can have a real impact on the industry. Doctoral programs prepare the individual to potentially have an impact on his or her career. Professional PhD candidates, depending on a concept to be explored in a given scientific field or a problem to be solved in the industry, choose their own research topic and then offer or propose solutions that can have a significant socio-economic impact on the community.
PhD courses also provide the conditions required to get high-level jobs and positions. A person qualified to have a PhD degree is someone who is eligible for a particular field or profession, and most of them previously had been in the position of making decision. Such a person currently seeks to refine and develop complex work skills at the workplace and be promoted at a higher level of decision making. A doctoral program transforms a person’s field of activity and enables him/her to think about complex problems and directly find optimal solutions for them.
A person undergoing a PhD program is able to exhibit skills at a higher level. Holding a doctoral degree not only shows the title, but also the holder of such a title should be able to demonstrate skills in high-quality writing and methods of research and data analysis, and extend his/her advanced skills in applied or clinical research settings. In most cases, having a professional doctorate degree and the scientific and practical qualifications can prove these skills. The method used may include identifying, analysing, expressing, and solving complex problems. PhD courses help students learn the method of analysing a problem/subject presented to them. Therefore, a trained person should be able to understand the relationship between factors affecting the problem more comprehensively.
A PhD candidate should also be able to establish and develop a professional network with his/her colleagues. Courses offered online or in-person with other classmates represent a wide range of areas and fields, by which participants are able to improve their professional skills. These people form a large professional network and can support each other in future work. Creating a competitive setting and placing applicants with different scientific orientations in a course or class will lead them to challenge each other and can elicit responses from the participants, and thus holding the course in group will have a better outcome than completing it individually [10].
In various countries, an important reason for obtaining a PhD degree is potentially to increase the current or future income of the degree holder. Many high-level jobs require a PhD degree. Therefore, people who spend their time and money to get a degree will benefit from its financial outcomes. While taking into account, the possible reasons for obtaining a degree, one must accurately assess the potential for future earnings and ensure the returns on his/her investment. It should be noted that PhD students are worthwhile, and various institutions need people with PhD degrees as they will help to obtain a better financial position and reputation. Therefore, such gifted and well-educated people must be treated fairly [11,12].
Problems Causing a PhD Student to be Deprived of this Degree
Lack of interest and motivation to attend the PhD course.
Overestimating or underestimating the requirements for the course entrance.
Non availability of a supervisor who is aware of the trends and requirements of the project.
The lack of regular contact with the supervisor.
Lack of sufficient reasons to continue studying and presenting a dissertation.
Engaging in a new job before completing the dissertation [13,14].
The most Important Facts to be Considered when Choosing a Thesis Topic
A. Assess the abilities of your supervisor based on his/her experience in conducting and completing graduate projects.
B. The applicant himself/herself should choose a thesis supervisor, and hence does not allow the institution to impose their opinion on him/her.
C. Stars may be attractive but not reachable as they are located in a very far away distance. So consider a supervisor who is not too much involved with other tasks.
D. A good supervisor is able to defend you in case of necessity.
E. Check the potential abilities of the supervisor and act cautiously with your project consultant professors.
Z. The instructor who is active in the field of the project is able to increase the progress of the work.
H. Educational institutions can allow PhD students to complete their projects outside the university.
T. Plan your weekly meetings with your supervisor.
Y. Having access to those who are fit for the topic you have chosen to work on [15,16].
Problems and Challenges which PhD Students Face Currently
There were approximately 21,343 doctoral students in 2007 in the USA and this number increased to 30,093 in 2013 by a 41% raise, with the highest increase found among graduates of the biological sciences. The 2014 report states that in the 34 countries that have established organisations for economic and developmental cooperation, this proportion has reached 1.6 percent (twice) from 0.8 percent of the country’s population over the past 17 years [17].
All of the PhD students are not looking for a university job, but the number of people who are seeking a position due to growth in the number of applicants for university education is relatively high. Despite growing number of graduates in various jobs, there is still no equilibrium between the number of PhD graduates and vacant occupations. The number of graduates whose initial enrollment was free and without employment undertaking was 42%, while it was 28% more than the same number in 2003. The total number of PhD graduates is more than the number required in various research fields [18].
Given this relatively disappointing career perspective faced by doctoral graduates, do people still have to pursue this degree? One reason to take PhD courses is that there is no place or thing that will keep their mind off of getting a doctorate degree. On the other hand, university faculty members in order to advance their occupation benefit from doctoral and post-doctoral students who are available free of charge and use academic credits and the time and energy spend by these students to conduct their research projects in accordance with international standards.
Four prominent professors in the United States have established a website on bioethical research that seeks to improve the quality of students of higher-education. In this website, while examining how effectively academic staffs are trained, it asks doctoral students, postgraduate students, and economists on how to prevent the expansion of the workforce at the PhD level. The founders of this website seek to thoroughly review PhD programs and the fields in which students are admitted and they want to work to organise this educational level. To this end, they skip minor changes and undertake making fundamental changes [19].
Studies have also evidenced that only one-third of the US higher education institutions possess information on the status of postgraduate students, and the rest of the institutions only have information about the time that students are studying [20].
Some scholars believe that the PhD program in Biological Sciences should be divided into two parts. The first part should focus on providing academic employment opportunities and the second part focus on training staffs that go into the depth of science and get involved in applied-operational business activities and other occupations. Those who have been trained for academic field, focus on the non-explicit components of the real world and discoveries, and other professional PhD holder can be useful in structured contexts and teaching specific skills [21].
This has happened in the field of engineering, where two different types of doctorate courses are offered: PhD in Engineering” to engage in academic jobs and “PhD for working in industries and supervising industrial activities”. The latter type is not only equivalent to the academic one, but also some believe that, because of their high skills, this group of graduates are more efficient and productive. As a result, employers and industry owners compete for attracting this group of engineers and have many better job offers for them. A misconception is that academic counterparts view doctoral engineers as being at a lower level, while technology companies consider academicians as inefficient for the real worlds. One of the important issues of PhD students is lack of both adequate supervision and communication with their supervisors. So, they require better interaction and support [17,22].
Employment of PhD Graduates
Most of the PhD students do not act purposefully. They don’t know what they are looking for and what kind of job is suitable for them. Issues such as job position, livelihood, and the time spent to get this degree are all key factors in pursuing this educational level [10]. A study on PhD graduates 5-10 years after their graduation showed that with the saturation of college jobs at this stage, the number of applicants who can be hired at universities reduced and the changes of pursuing a PhD course in biological sciences has been reduced. Accordingly, PhD graduates are more likely to turn to self-employment, public employment, and so-called non-profit jobs [23].
Having detailed information on post-graduate conditions obtained from academic sources and the national statistical office, students can, with open mind, evaluate future job titles and financial opportunities, and with this information can learn about the status of other graduates, their occupations, their workplace and income levels. This information requires government investment and support, and it is now apparent from surveys that graduates are still willing to work in higher educational institutions.
During the doctoral program, students need to consult with each other in a group and organise workshops on the management, interviewing, and use of the Internet to analyse their professional goals. These workshops can transform the person from a student into practical professionals, and show strategies to enable them to apply for appropriate jobs and positions, and learn skills required for his/her future activities. They can also know the actions that can be potentially taken by people with similar qualifications. Of course, there are always many job opportunities for people who have completed their doctoral degree and have a good mind [21,24].
The Education System in Iran
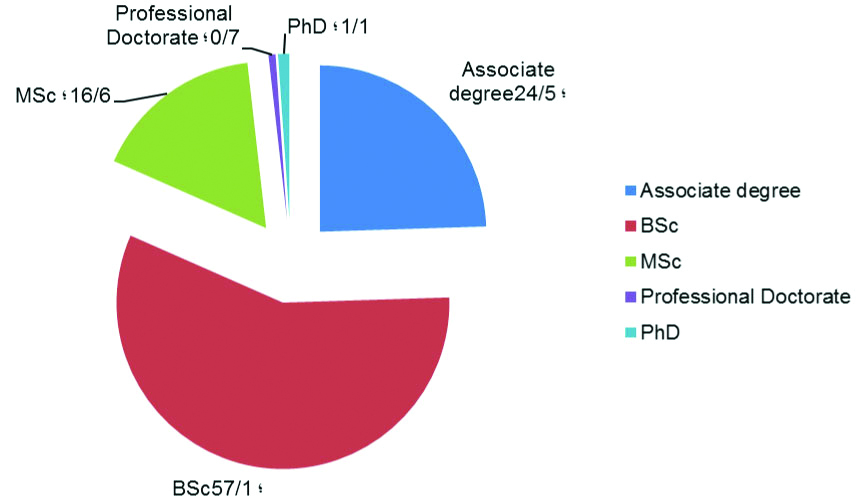
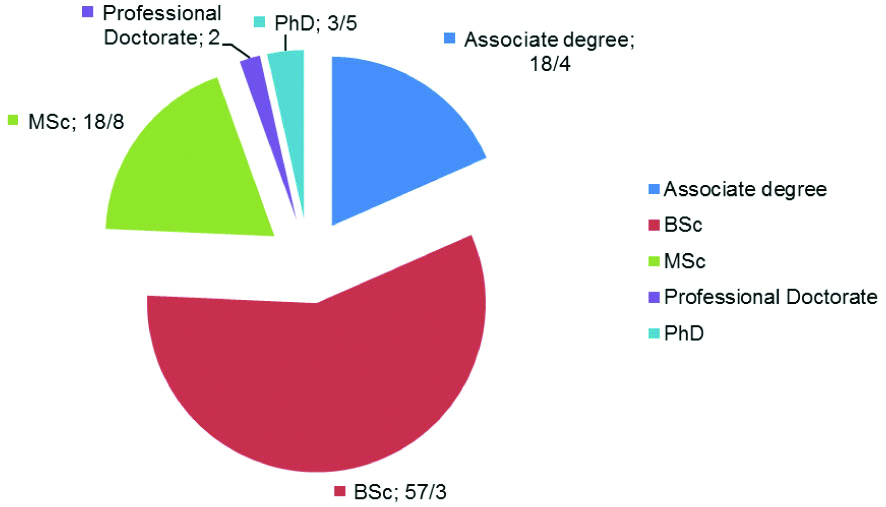
Due to the fact that Iranians continue to enjoy higher education and Iran has a poor educational system, it is necessary to discuss the situation of continuing education at the highest level, PhD. In the academic year of 2005-2006, there were 19,237 PhD students; in the year 2012-2013, this number reached to 58,683. These students were studying in 2,521 different disciplines at universities across the country [25], and in the academic year of 2015-2016, it reached to 71,914 students [26]. [Table/Fig-2] summarises the frequency (%) of graduated University students according to the level of education during 2015-2016 [26] and [Table/Fig-3] shows the frequency (%) of university students according to the level of education during 2016-2017 [27].
Frequency (%) of graduated University students according to the level of education during 2015-2016 (Adopted from Institute for research and planning of higher education) [26].
Frequency (%) of university students according to the level of education during 2016-2017 (Adopted from Institute for research and planning of higher education) [27].
PhD students in 2013 accounted for 1.56% while in 2015 they constituted 1.98% of the total students (4,802,721 students) [26]. Evaluating challenges faced by PhD students is important. This will help prospect applicants take more informed decision about pursuing the PhD program.
In the higher education system of Iran, PhD candidates can apply for the course in various ways as:
Admission through an entrance test. In this method, the admission processes of students are made only through the national curriculum that is annually held by the National Organisation for Educational Testing, and the admitted applicants will finally be introduced by this organisation to the universities.
The list of the applicants who enter the university through free admission without taking the entrance test (through internal examination, interviews, or a review of the scientific qualifications), individuals whose names are sent to universities by the Ministry of Science, Research and Technology [28].
There were 120,000 PhD students in 2012 and according to the United Nations Meeting on Trade and Development, only 60,900 PhD students were studying in 2013 [29], but according to our national statistics, there were 58,683 students [27], and 73,437 PhD students in 2013-2014 academic year [30]. The number of PhD students during the academic year of 2015-2016 was 115,191. In the academic year of 2016-2017 and 2017-2018 in both public and private universities and institutions, were 140,558 and 141,077 students, respectively [27].
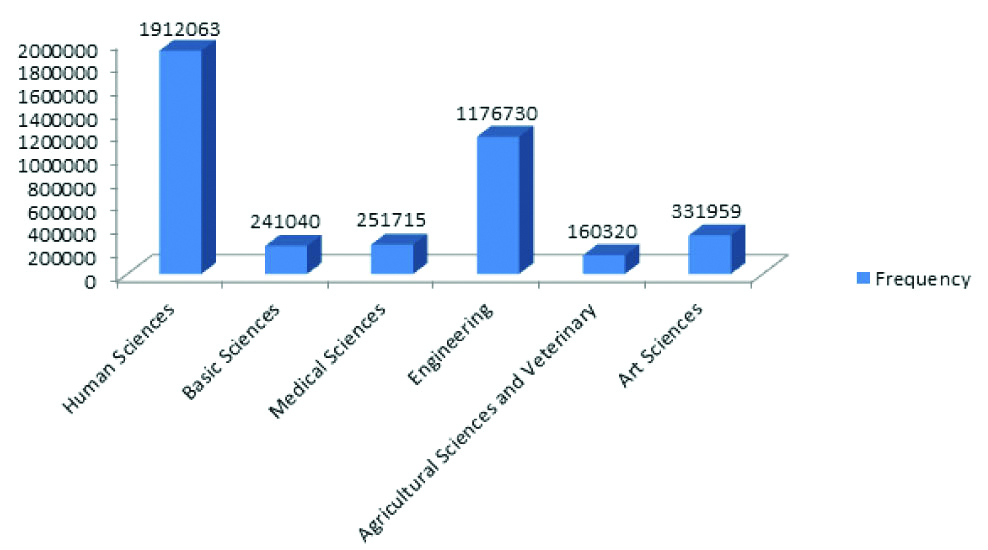
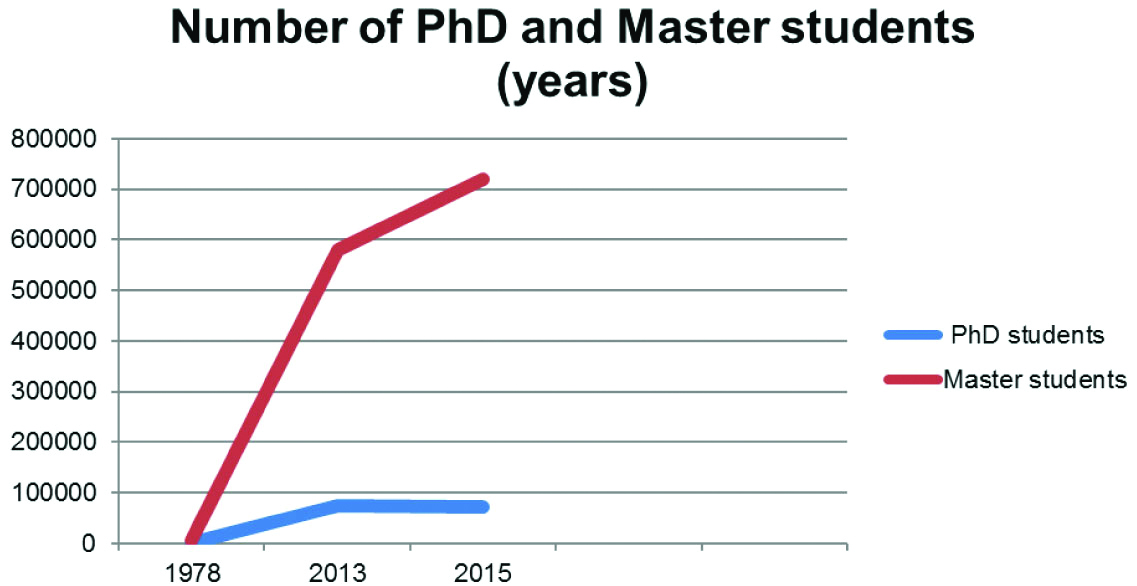
During the academic year 2013-2014, Iranian students with associate, bachelor, and master degrees enrolling for a professional doctorate degree including medicine were 22.3%, 62.3%, and 12.4%, respectively, not to mention approximately 3% of all the students enrolling for the same program [26]. [Table/Fig-4] summarised the frequency of university students according to the field of education during 2016-2017 (Adopted from Institute for research and planning of higher education [27]. Also, [Table/Fig-5] shows the number of university students at the level of Master and PhD during three reported episodes [26].
Frequency of university students according to the field of education during 2016-2017 (Adopted from Institute for research and planning of higher education [27].
Number of university students at the level of Master and PhD during 3 reported episodes [26].
Discussion
A postgraduate degree is greatly important for applicants and they must choose a topic for the PhD dissertation based on their educational background and field of study. If national and international problems are addressed, then there is no need to obtain a doctorate degree, and the applicants with a master’s degree can be attracted to public and private institutions. Therefore, in many countries such as Norway, Sweden and Denmark, not completing a PhD program is not considered as a disadvantage and failure, because people who seek a job or tend to work in an academic field can complete advanced scientific courses and engage in both professional and research activities. To meet the community’s need, applicants can go through a two-year training course and thus they do not need to spend 4, 5 or more years to get the required qualifications [22].
In many countries, however, a master’s degree is considered to be lower than a doctorate degree, and thus, universities are more interested in launching doctoral programs. Between 2000 and 2011, Masters in Science and Engineering increased by 57%, while PhD programs increased by 38% [17].
Universities have trained masters who can simultaneously develop their scientific and professional skills. A number of universities across the United States conduct undergraduate research training courses designed to help them decide on a doctorate, a professional doctorate, or a transition to industry. However, a master’s degree cannot meet the needs of individuals to continue their education. In Europe and North America, many universities demand tuition from applicants for a postgraduate degree, which leaves many students unable to continue their studies. For years, economic decision-makers have been blocking entry into the life science courses, and now they are holding these courses and believe that biomedical research should be saved. But limiting access to education can also provide irreparable damage to the advancement of science and society [31].
The financial support body for postgraduate courses in the field of biomedicine can play an important role in restricting educational institutions offering PhD courses, and have complete supervision on the supply and demand for courses and programs. Some believe that if students spend even a bit of money to study for a degree, they may feel more responsible for what they do and wonder if this course is appropriate for them. But this can be a contradictory and even controversial issue, depriving some candidates from academic growth and development, and even those with high abilities and talents but at spending a cost may motivate students to make more efforts in their studies. Nevertheless, those who cannot afford the cost of a doctoral degree can be recommended that next year they will be able to apply for a scholarship with another exam or paper, and with comprehensive information they obtain during the waiting period, they can plan their studies and guarantee the future of research in various fields, including medicine [32,33].
Conclusion(s)
A brief history of the donation and its granting documents was presented in this review. PhD degree, its present types and the required qualifications were also reviewed. In many disciplines, applicants with both BSc and MSc degrees can apply for a doctorate course, but the most common trend is master degree. In the field of engineering, there are two paths to doctoral graduates: university and industry. However, more employment is available to those who choose to work in the industry. The goals, the necessities, and the benefits of having a doctoral degree, as well as the problems faced by students were discussed. Also, some suggestions were provided for prospect applicants on how to choose a topic for their dissertation and how to solve the problems faced by them followed by a discussion of the employment prospect of PhD candidates. Finally, the educational system in Iran was discussed, and the authors concluded that holding doctoral courses and having people with a doctoral degree is valuable only when they can expand the boundaries of knowledge or solve society’s problems, otherwise, an individual with a master’s degree can significantly address the problems facing the community.
[1]. Nerad M, The PhD in the US: Criticisms, facts, and remediesHigh Educ Policy 2004 17(2):183-99.10.1057/palgrave.hep.8300050 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[2]. Kietrys KA, Hildegart in the 1930s: Her politics and her imageBull Hisp Stud 2015 92(3):255-82.10.3828/bhs.2015.17 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[3]. Hawk BW, The literary contexts and early transmission of the Latin life of JudasJMRC 2018 44(1):60-76.10.5325/jmedirelicult.44.1.0060 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[4]. Cobban AB. The medieval English universities: Oxford and Cambridge to c. 1500: Routledge. eBook published 2017 [Google Scholar]
[5]. Casanave CP, Taking risks? A case study of three doctoral students writing qualitative dissertations at an American university in JapanJSLW 2010 19(1):1-16.10.1016/j.jslw.2009.12.002 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[6]. Stiwne EE, Alves MG, Higher education and employability of graduates: will Bologna make a difference?Eur Edu Res J 2010 9(1):32-44.10.2304/eerj.2010.9.1.32 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[7]. Chen Hl, The perspectives of higher education faculty on WikipediaElectron Libr 2010 28(3):361-73.10.1108/02640471011051954 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[8]. Harris C, Ravenswood K, Myers B, Glass slippers, Holy Grails and Ivory Towers: gender and advancement in academiaLabour & Industry: A Journal of the Social and Economic Relations of Work 2013 23(3):231-44.10.1080/10301763.2013.839084 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[9]. Peacock S, The PhD by publicationIJDS 2017 12:123-35.10.28945/3781 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[10]. Auriol L, Careers of doctorate holders: employment and mobility patternsOECD Science, Technology and Industry Working Papers 2010 2010(4):0_1 [Google Scholar]
[11]. Rezaeian M, Introduction to PhD ProgramRazi J Med Sci 2011 269(5):45-48. [Google Scholar]
[12]. Barnacle R, Mewburn I, Learning networks and the journey of ‘becoming doctor’Studies in Higher Education 2010 35(4):433-44.10.1080/03075070903131214 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[13]. Sverdlik A, Hall NC, McAlpine L, Hubbard K, The PhD experience: A review of the factors influencing doctoral students’ completion, achievement, and well-beingIJDS 2018 13:361-88.10.28945/4113 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[14]. Prazeres F, PhD supervisor-student relationshipJ Adv Med Educ Prof 2017 5(4):220-21. [Google Scholar]
[15]. Brailsford I, Motives and aspirations for doctoral study: Career, personal, and inter-personal factors in the decision to embark on a history PhDIJDS 2010 5(1):16-27.10.28945/710 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[16]. Rezaeian M, How to supervise a medical thesisWorld Family Medicine Journal: Incorporating the Middle East Journal of Family Medicine 2014 99(1196):01-03.10.5742/MEFM.2014.92492 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[17]. Gould J, How to build a better PhDNature News 2015 528(7580):22-25.10.1038/528022a26632571 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
[18]. Pyhältö K, Toom A, Stubb J, Lonka K, Challenges of becoming a scholar: A study of doctoral students’ problems and well-beingISRN Edu 2012 1-12:93494110.5402/2012/934941 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[19]. Barnacle R, Cuthbert D, Laurie R, Exploring researcher motivation: Implications for PhD educationAsia Pacific Graduate Education: Springer 2016 :199-215.10.1057/978-1-137-54783-5_12 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[20]. de los Santos Jr AG, Cuamea KM, Challenges facing Hispanic-serving institutions in the first decade of the 21st centuryJLE 2010 9(2):90-107.10.1080/15348431003617798 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[21]. Sauermann H, Stephan P, Conflicting logics? A multidimensional view of industrial and academic scienceOrg Sci 2013 24(3):889-909.10.1287/orsc.1120.0769 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[22]. Thune T, The training of “triple helix workers”? Doctoral students in university–industry-government collaborationsMinerva 2010 48(4):463-83.10.1007/s11024-010-9158-7 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[23]. Vedder R, Denhart C, Robe J, Why are recent college graduates underemployed? University Enrollments and Labor-Market RealitiesCCAP 2013 [Google Scholar]
[24]. Cyranoski D, Gilbert N, Ledford H, Nayar A, Yahia M, Education: The PhD factoryNature news 2011 472(7343):276-79.10.1038/472276a21512548 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
[25]. Science, Technology and Innovation Policy Review. UNCTAD. The Islamic Republic of Iran. Retrieved from: https://unctad.org/en/PublicationsLibrary/dtlstict2016d3_summary_en.pdf. available at 22-8-2019 [Google Scholar]
[26]. Statistics. The ministry of science, research and technology. Retrieved from: https://www.msrt.ir/en/page/20/statistics#us1978. available at 22-8-2019 [Google Scholar]
[27]. Statistics. Institute for research and planning of higher education. Retrieved from: https://irphe.ac.ir/index.php?sid=1&slc_lang=en. available at 22-8-2019 [Google Scholar]
[28]. Davari H, Aghagolzadeh F, To teach or not to teach? Still an open question for the Iranian education systemEnglish Language Teaching in the Islamic Republic of Iran: Innovations, Trends, and Challenges 2015 :13-9. [Google Scholar]
[29]. Akhondzadeh S, Ebadifar A, Eftekhari MB, Falahat K, Medical science and research in IranArch Iran Med 2017 20(11):665-72. [Google Scholar]
[30]. Higher Education in Iran. The ministry of science, research and technology, Retrieved from: http://ir-de.iust.ac.ir/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/101-MSRT_SalarAmoli.pdf. available at 22-8-2019 [Google Scholar]
[31]. Keshavarz M, Management development of internal evaluation in the Islamic Republic of Iran (case study)Edu Res Rev 2011 6(14):804-11. [Google Scholar]
[32]. Bunce L, Baird A, Jones SE, The student-as-consumer approach in higher education and its effects on academic performanceStud High Educ 2017 42(11):1958-78.10.1080/03075079.2015.1127908 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
[33]. Brooksbank C, Janko C, Johnson C, See W, Lindén HH, Hardman M, LifeTrain: driving lifelong learning for biomedical professionalsJ Med Dev Sci 2015 1(2):01-07.10.18063/JMDS.2015.02.001 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]