In Acute Ischemic Stroke (AIS), recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator (rTPA) is used within 4.5 hours of onset of stroke. Its affordability, availability and time constraint make it of limited use [1]. There is need of universally available, affordable alternative drug which should be having long time period (fifth post stroke day) of utility with minimum adverse effect. NO may provide promising results.
Locally NO can be provided directly (inhaled) or systemic. Inhaled NO is neuroprotective in the developing brain, with reduction in the size of excitotoxic and ischaemic lesions in rats [10-13].
Three isoform of NOS exists: endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS), neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase (nNOS), and inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS). eNOS and nNOS are neuroprotective and iNOS is neurotoxic [14-20]. iNOS (neurotoxic) is expressed in macrophages, glial cells and tumour cells in response to pro inflammatory cytokines or endotoxin [20] and unlike eNOS and nNOS it is not expressed unless induced by cytokines or other agents. It can produce a large amount (100–1000 times greater) of NO in relation to eNOS and nNOS, due to its independence from calcium dependent mechanisms for activation. After induction, iNOS continuously produces NO until the enzyme is degraded. iNOS peak concentrations occur around one to two days after the injury in rats and recent study showed that iNOS is also expressed in human brain at two to eight days after Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) [20]. Two times greater NO level was detected in wild-type versus iNOS knockout animals [21]. Patients with higher levels went on to have a worse outcome [20] which proves the version “NO is a double edged sword”.
Having these scientific facts in our mind, we organised a study on MCAO model of rats with aim to find treatment at later stage of stroke (on fifth day) by the use of intracarotid artery injection of SNP ipsilateral to MCAO rat model.
Materials and Methods
This prospective study has been done from May 2015 to April 2016 at CSIR-CDRI, Lucknow, India on Sprague Dawley rats.
A total of 24 rats 250 gm to 280 gm were procured from the National Laboratory Animal Centre of CSIR-CDRI, Lucknow, India and experiments were performed after necessary approval of the Institute Animal Ethical Committee. Rats were allowed free access to food and water.
Animal grouping: Three groups were made for study [Table/Fig-1]
Flow chart of animal grouping.
(one-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), followed by Newman-Keuls test. Graph Pad prism (version-5.0) was used to statistical analysis. The p<0.05 was considered statistically significant)
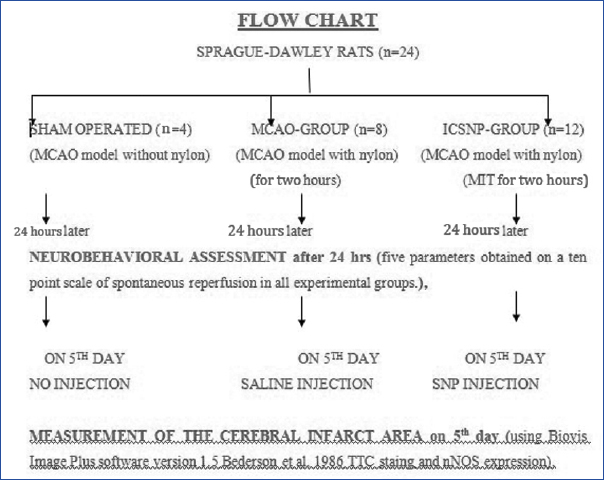
Sham operated (n=4);
MCAO-Group (n=8);
Sodium Nitroprusside treated ICSNP-Group (n=12).
Sham group were those in which all surgical procedure was carried out as in MCAO model except insertion of nylon filament. MCAO group were those in which all surgical procedure were carried out, middle cerebral artery was blocked by insertion of filament for two hours. Saline was given on fifth day of procedure.
ICSNP group were those in which MCAO surgical procedure (MCAO model with nylon) was done using Modified Intraluminal Technique (MIT). ICSNP was given after fifth day of stroke. Sodium nitroprusside was given directly in ECA by stump-technique and wound closed.
To get maximum ICSNP treated rats in minimum time the sample size varied.
Induction of ischemia/reperfusion (I/R): Rats were anaesthetized and focal cerebral ischemia was induced by MCAO using modified intraluminal technique (Longa EZ et al., 1989) [23]. Upon regaining light reflex, the animals were returned to cages.
Neurobehavioural assessment: The neurobehavioural assessment was performed after MCAO (two hours post MCAO procedure before placing the rats to the cages), before and after ICSNP procedure (to get the exact improvement by ICSNP), according to method developed by Longa EZ et al. [23]. Upon regaining light reflex (by putting torch light in eyes the pupils should contract), animals returned to cages. Briefly, the neurobehavioural findings were scored on five point scale with 10 grading scores: a score of 0 indicated no neurologic deficit, a score of 1 (failure to extend opposite forepaw fully) a mild focal neurologic deficit, a score of 2 (contralateral circling) a moderate focal Neurological Deficit (ND), a score of 3 (falling to the opposite side to the damage when hanged on net) a severe focal deficit and rats with a score of 4 did not walk spontaneously and had a depressed level of consciousness. The scores of neurobehavioural findings obtained after testing on each scale were summed up and denoted as neurological deficit score (Bederson JB et al., 1986) [24].
The animals showing no sign of neurological deficit were excluded from the study.
Measurement of the cerebral infarct area: After predetermined time point of I/R, the brains were quickly removed same day that is on fifth day post MCAO and after ICSNP injection and sliced into coronal sections at 2 mm intervals. Each slice was immersed in a 1.0% solution of 2, 3, 5-TTC for 30 minutes at 37ºC and then fixed in 10% buffered formaldehyde solution. The stained brain slices were digitally photographed and the infarct area was measured on posterior surface of each section using Biovis Image Plus software version 1.5. The percentage infarct area was calculated by subtracting the outlined white area from ipsilateral area of the hemisphere of affected side of the brain divided by ipsilateral area and multiplied by hundred. (Bederson JB et al.,) [24]. Also, nNOS expression was done to assess the usage of nNOS enzyme by NO.
Statistical Analysis
Mean±SEM was calculated and the statistical analysis was done by One-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), followed by Newman–Keuls test. Graph Pad prism (version.5.0) was used for statistical analysis. The p<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
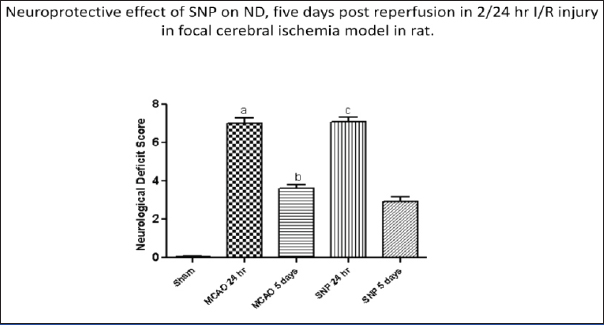
The effect of ICSNP on fifth day in ischemic stroke model was evaluated. ND scoring was analysed on the basis of neurobehavioural changes categorized into five parameters obtained on a ten point scale after 24 hour of reperfusion in all experimental groups. The [Table/Fig-2] shows neurological deficit and reduction in infarct size. The percentage improvement ND score in control group was 51.42% while in ICSNP group it was 59.15%. ND was improved greater in drug treated group showing beneficial effect of drug administration [Table/Fig-2].
The comparison of neurological deficit (ND) and % reduction in infarction size. The ND is less in the test group than control group.
| S No | Type | N | ND | % Reduction In Infarction Size |
|---|
| 24 hrs | 5 Days |
|---|
| 1 | SHAM | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0.98 |
| 0 | 0 | 0.77 |
| 0 | 0 | 0.67 |
| 0 | 0 | 0.44 |
| Mean | 0 | 0 | 0.71 |
| 2 | MCAO | 8 | 7 | 3 | 65.800 |
| 6 | 4 | 55.450 |
| 8 | 4 | 63.110 |
| 7 | 4 | 63.360 |
| 6 | 3 | 68.260 |
| 7 | 4 | 59.010 |
| 8 | 3 | 60.340 |
| 7 | 4 | 61.770 |
| Mean | 7 | 3.6 | 62.13 |
| 3 | ICSNP | 12 | 7 | 3 | 38.27 |
| 6 | 4 | 24.81 |
| 8 | 3 | 49.38 |
| 7 | 4 | 36.64 |
| 6 | 3 | 52.08 |
| 8 | 3 | 42.22 |
| 7 | 4 | 22.92 |
| 8 | 3 | 28.24 |
| 7 | 2 | 30.43 |
| 7 | 3 | 26.81 |
| 6 | 2 | 24.71 |
| 8 | 1 | 21.87 |
| | Mean | 7.1 | 2.9 | 33.19 |
| | %Change | | 10.44% | 46.57% |
MCAO: Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
ICSNP: Intracarotid Sodium Nitroprusside
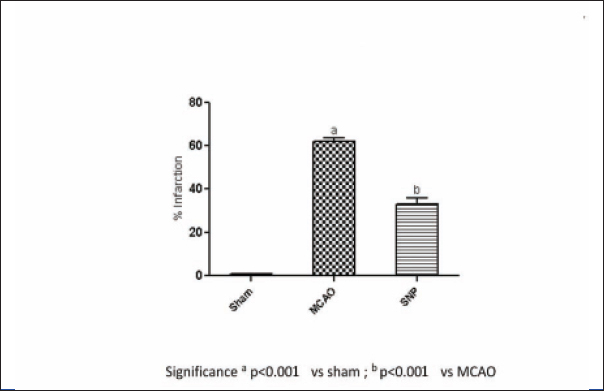
The area of infarction due to ischemic insult was assessed by TTC staining. The TTC unstained area representing infarct was measured and presented as percentage reduction in infarct area. Control group produced an infarct size of almost 62.13% in ipsilateral side of control rat brain as compared to the contralateral side. The ICSNP group showed the cerebral infarction to 33.19% [Table/Fig-2].
The comparison between the two treatment groups for reduction of percentage of infarction shows significant changes (significance p<0.001 vs sham, and p<0.001 vs MCAO after six hours) [Table/Fig-3,4].
Neuroprotective effect of SNP on ND, five days post reperfusion in 2/24 hour I/R injury in focal cerebral ischemia model in rat.
*Significance a p<0.001 vs SHAM; b p<0.001 vs SHAM; p<0.05 vs MCAO 24 hours
Neuroprotective effect of SNP on % infarction, five days post reperfusion in 2/24 hour I/R injury in focal cerebral ischemia model in rat.
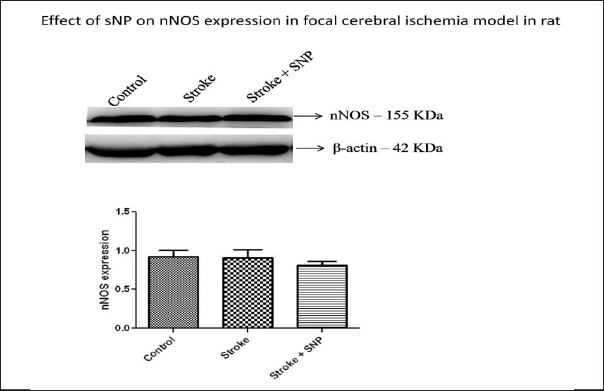
The expression of nNOS was also done to assess the nNOS usage by nitric oxide. [Table/Fig-5] shows nNOS expression in focal cerebral ischemia model. It did not show any significant improvement [Table/Fig-5]. None of the rats died during this experiment.
Effect on nNOS expression in focal cerebral ischemia model.
Discussion
SNP being a NOD acts as postsynapse’s NOS and releases NO which acts presynaptically and generates the impulse via 10,000 fold effect reduces the infarct size thus improves the Neurological Deficit (ND), even after fifth post stroke day. This issue is obviously important for the evaluation of stroke patients reach medical attention very late (more than 4.5 hour) after the occurrence of cerebral ischemia in which penumbra is still salvageable.
SNP is a universally available and affordable NOD drug with minimum adverse effect. We tested its utility in the later stage of stroke to be useful from fifth day.
It was earlier demonstrated that intracarotid administration of the NO generating agents SNP and 3-morpholinosydnonimine (SIN-1) which increases Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF) in the ischemic territory and reduces the size of the infarct resulting from occlusion of the Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) in the rat in acute cases [25,26]. In further experiment [27] NOD SIN-1 donor were administered 3, 15, 30, 60 or 120 minutes after MCA occlusion.
The reduction in infarct size and enhanced recovery of CBF and EEG amplitude by SIN-1 was seen when SIN-1 was administered 3, 15, 30, and 60 minutes after MCA occlusion (p<0.05). However, administration of SIN-1 two hours after MCA occlusion did not affect the size of the infarct (p>0.05). Authors concluded that post treatment with SIN-1 was effective in reducing focal ischemic damage only if this agent was administered up to 60 minutes after MCAO.
The “protective” effect is dose-related and is specific for NO donors because the NO-independent vasodilator papaverine does not reduce the size of the infarct [25]. Infusion of NO donors does not affect platelet aggregation, assessed ex vivo [25]. These observations indicate that NO donors protect the ischemic tissue at risk for stroke by enhancing collateral flow to the ischemic territory (penumbra) and raise the possibility that these agents could be used in the treatment of acute cerebral ischemia.
Studies showed that synaptic cleft’s superoxide formation [22] is being neutralised by the serum superoxide dismutase (after crossing blood brain barrier) tends to decrease upto five days post stroke and its serum level again comes to normal after that.
iNOS (neurotoxic) can produce large amount (100–1000 times greater) and continuously NO in relation to eNOS and nNOS, due to its independence from calcium dependent mechanisms for activation until the enzyme is degraded after induction, peak concentrations occur around one to two days [21].
These authors [25-27] have not considered iNOS and superoxide formations at the synaptic region which have a very important detrimental effect on synaptic activity by inhibiting the anterograde neurotransmission upto five days post stroke.
In our MCAO model we have taken care of iNOS and superoxide both by just holding the rats for five days safely and then giving intracarotid SNP. Also, instead of using SIN-1 we have used SNP as a NOD which shows the Long Term Potentiation (LTP) effect at synapse level via 10,000 fold effect thereby reducing the size of infarct.
In ischemic stroke, the maximum effect can be obtained by passing eNOS of various systemic vessels and heart (to avoid cardiovascular instability - hypotension). So ipsilateral to ischemic stroke, intracarotid injection was given in appropriate dose. The NO produced hereby, at the infarct tissue locally, acted promptly through 10,000 fold effect and LTP, thus impulse generated.
Control group produced an infarct size of almost 62.13% in ipsilateral side of control rat brain as compared to the contralateral side. The treatment of rats with SNP showed the cerebral infarction to 33.19% as compared to the contralateral side. At six hours post injection the various significance reading is as below (significance p<0.001 vs sham, and p<0.001 vs MCAO six hours). It means that infarct size reduced by 53.42% as compared to control. The reduction in infarction area may due to improved NVC due to activation of beneficial nitric oxide (nNOS and eNOS) locally and blood supply to penumbra region or via 10,000 fold effect.
The percentage improvement in ND score in control group was 51.42% while in ICSNP group it was 59.15%. The neurological deficit was improved greatly in drug treated group showing beneficial effect of drug administration. The nNOS expression was not found to have any difference between two groups (B and C). The nNOS probably do not have any role in late stages of stroke in rats or our tests were not upto the mark to test the smallest change in nNOS expression or it may be possible in humans due to evolutionary difference in enzymes than to rats but exact mechanism is still to be evaluated.
Limitation
The limitations of this study were the number of rats itself and not able to evaluate the 10,000 fold effect via PNSAS, and non availability of the PNSAS at our setup.
Conclusion
ICSNP reduces infarction by about 53.42% and neurological deficit by 13.07% in ICSNP-Group as compared to control on fifth post ischemic stroke day. It is a swift-acting drug in the treatment of focal stroke acts even after five days when iNOS’s and superoxide’s functions cease but no effect on nNOS expressions. In view of the above findings we recommend the use of ICSNP in humans on fifth post stroke day cases via ipsilateral intracarotid artery in very low dose as a stat injection with every precaution either direct or via femoral Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA).
MCAO: Middle Cerebral Artery OcclusionICSNP: Intracarotid Sodium Nitroprusside