Basic Principles of Obstetric Anesthesiology: A Crossword Puzzle
Jennifer Wright1, Allan F. Simpao2, Omar Viswanath3
1 Anesthesiology Attending Physician, Department of Anesthesiology, Miami Beach Anesthesiology Associates, Inc., Mount Sinai Medical Center, Miami Beach, Florida, USA.
2 Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology and Critical Care, Perelman School of Medicine, The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and The University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA.
3 Anesthesiology Chief Resident Physician, Department of Anesthesiology, Mount Sinai Medical Center, Miami Beach Anesthesiology Associates, Inc., Miami Beach, Florida, USA.
NAME, ADDRESS, E-MAIL ID OF THE CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: Dr. Omar Viswanath, Anesthesiology Chief Resident Physician, Department of Anesthesiology, Miami Beach Anesthesiology Associates, Inc., Mount Sinai Medical Center, Miami Beach, Florida, USA.
E-mail: viswanoy@gmail.com
OBSTETRIC ANAESTHESIA

Across
Magnesium sulfate is used to treat PIH and also used as a ________.
Evaluation of fetal well-being with the purpose of detecting changes in fetal activity due to asphyxia.
This medication is effective for uterine relation during removal of retained placental tissue.
Neither succinylcholine nor non-depolarizing NMBDs cross the placenta because they are highly.
A decrease of this to 80% of the nonpregnant value at term can lead to the rapid development of maternal hypoxemia following apnea associated with the induction of general anesthesia.
This medication is the treatment for magnesium toxicity.
Engorgement of this epidural plexus makes puncture of cannulation of an epidural vein more likely and contributes to a higher level of local anesthetic spread.
High levels of this hormone delay gastric emptying and decrease lower esophageal tone increasing the risk of aspiration.
This deceleration of fetal heart rate is caused by head compression.
Exteriorization of the uterus increases the risk of this complication.
Down
This local anesthetic decreases the quality and duration of analgesia from subsequently administered epidural narcotics.
After intrathecal administration, respiratory depression with morphine exhibits this pattern as opposed to the lipophilic fentanyl that can cause early respiratory depression but not late.
Prevented by lateral uterine displacement.
First line drug in the management of uterine atony, this medication’s side effects include tachycardia, hypotension and EKG changes with rapid (bolus) administration.
This deceleration in fetal heart rate associated with hypoxia is caused by uteroplacental insufficiency.
Pain during this stage of labour is carried by visceral afferent fibers T10-L1 and is caused by uterine contractions and cervical dilation.
This declaration of fetal heart rate is caused by cord compression.
Hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelets.
Pain during this stage of labor is due to stretching of the birth canal, vulva, and perineum and is conveyed by the afferent fibers of the posterior roots of the S2-S4 nerves.
This medication is the induction agent of choice for a parturient with significant hemorrhage or acute asthma symptoms requiring general anesthesia.
Avoid the use of this medication for the management of postpartum hemorrhage in patients with asthma.
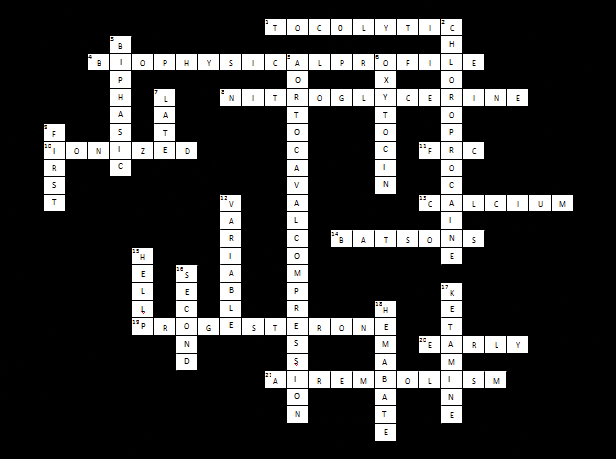
ANSWERS OBSTETRIC ANAESTHESIA
[1]. Birnbach DJ, Browne IM, Anesthesia for obstetrics. In: Miller RD, editorMiller’s Anesthesia 2005 New YorkElsevier/Churchill Livingstone:2203-41. [Google Scholar]
[2]. Birnbach DJ, Ostheimer GJ, Ostheimer’s Manual of Obstetric Anesthesia 2000 New YorkChurchill Livingstone [Google Scholar]